Aur
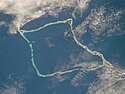
 Atol Aur na zdjęciu z promu kosmicznego Columbia w 1983 roku | |
| Państwo | |
|---|---|
| Akwen | Ocean Spokojny |
| Powierzchnia | 5,62 km² |
| Populacja (2011) • liczba ludności | 499 |
Aur – zamieszkany atol na Wyspach Marshalla. Należy do archipelagu Ratak Chain na Oceanie Spokojnym. Według danych za rok 2011 atol zamieszkiwało łącznie 499 osób (spadek w stosunku do 1999 roku, kiedy to liczba ta wynosiła 537), na wyspach znajdowało się 95 domów[1]. Zlokalizowany jest tu także port lotniczy z pasem startowym o długości 640 m (kod IATA: AUL)[2].
Atol został odkryty przez kapitana Johna Marshalla w 1788[3].
Geografia
Aur leży na południe od atolu Maloelap. Składa się z trzech głównych wysp: Tabal, Aur i Bigen oraz 39 mniejszych (według innego źródła wysp jest 43[4]) m.in. Pokonaen, Anedik, Piganman, Baojen, Majruon, Enob, Ajej, Nanalle, Arjal, Mummet[5] o łącznej powierzchni 5,62 km². Łączna powierzchnia laguny wynosi 239,78 km²[6], a jej maksymalna głębokość to ponad 80 m. Istnieją dwie główne drogi morskie łączące lagunę z otwartym oceanem: od strony zachodniej i południowej[7]. W przeszłości atol określano nazwami: Aurh, Ibbeson, Ibbetson's Island i Traversey[6].
W 1967 r. stwierdzono występowanie na Aur 7 gatunków ptaków, w tym 6 potencjalnie lęgowych[5]. Na atolu spotkać można następujące gatunki roślin: Catharanthus roseus, Centella asiatica, Colocasia esculenta, Eragrostis amabilis, Ipomoea violacea i Ixora coccinea[8].
Przypisy
- ↑ Economic Policy, Planning, and Statistics Office, Office of the President: The RMI 2011 Census of Population and Housing. Summary and Highlights Only (ang.). U.S. Department of the Interior, 2012-02-14. [dostęp 2016-07-26]. [zarchiwizowane z tego adresu (2020-03-02)].
- ↑ AUL - Aur Island, MH - Airport - Great Circle Mapper (ang.). Great Circle Mapper. [dostęp 2016-07-26].
- ↑ Max Quanchi, John Robson: Historical Dictionary of the Discovery and Exploration of the Pacific Islands. Lanham, Maryland; Toronto; Oxford: The Scarecrow Press, Inc., 2005, s. XX. ISBN 0-8108-5395-7.
- ↑ Republic of the Marshall Islands - Aur Atoll (ang.). Republic of the Marshall Islands Embassy, USA, 2002. [dostęp 2016-07-26].
- ↑ a b A. Binion Amerson Jr.: Atoll Research Bulletin No. 127: Ornitology of the Marshall and Gilbert Islands. Waszyngton, U.S.A.: The Smithsonian Institute, 1969, s. 94–96. (ang.)
- ↑ a b Atoll Information--Aur Atoll (Marshall Islands) (ang.). marshalls digital micronesia, 1999. [dostęp 2016-07-26].
- ↑ Marshall Islands - Aur (ang.). the island encyklopedia. [dostęp 2016-07-26].
- ↑ Plant Threats to Pacific Ecosystems: Aur Atoll (ang.). Hawaiian Ecosystems at Risk project. [dostęp 2016-08-01].
Linki zewnętrzne
- Historic Maps of the Marshall Islands. Map of Aur Atoll 1893 (ang.). marshalls digital micronesia, 2002. [dostęp 2016-07-26].
Media użyte na tej stronie
Autor: Uwe Dedering, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Relief location map of Oceania.
- Projection: Lambert azimuthal equal-area projection.
- Area of interest:
- N: 35.0° N
- S: -55.0° N
- W: 110.0° E
- E: 230.0° E (This is -130° E)
- Projection center:
- NS: -10.0° N
- WE: 170.0° E
- GMT projection: -JA170/-5/20c
- GMT region: -R79.58168799459713/-44.42200097096855/-120.83787447194456/33.90289238708686r
- GMT region for grdcut: -R80.0/-63.0/260.0/39.0r
- Relief: SRTM30plus.
- Made with Natural Earth. Free vector and raster map data @ naturalearthdata.com.
Autor: NordNordWest, Licencja: CC BY 3.0
Location map of the Marshall Islands
Atol Aur w archipelagu Wysp Marshalla