Australopithecus africanus
| Australopithecus africanus | |
| Dart, 1925 | |
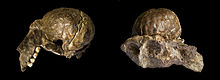
 Czaszka Australopithecus africanus | |
| Systematyka | |
| Domena | |
|---|---|
| Królestwo | |
| Typ | |
| Podtyp | |
| Gromada | |
| Rząd | |
| Rodzina | |
| Podrodzina | |
| Rodzaj | |
| Gatunek | Australopithecus africanus |
Australopithecus africanus – gatunek australopiteka znany już od 1924 roku dzięki odkryciu tzw. „Dziecka z Taung” przez Raymonda Darta w Taung (RPA). W 1947 roku, również w RPA, Robert Broom i John T. Robinson odkryli czaszkę o tych samych charakterystykach co znalezisko Darta, którą nazwali „Pani Ples", znaleziskiem tym potwierdzając istnienie australopiteków na południu Afryki.
Opis
Osobniki męskie tego gatunku ważyły ok. 41 kilogramów i dorastały do 138 cm, a żeńskie ok. 30 kg i dorastały do ok. 115 cm.
Australopithecus africanus żył przeszło 3 mln lat temu. Być może gatunek ten występował jeszcze 2 mln lat temu. Przedstawiciele tego gatunku poruszali się na dwóch nogach choć prawdopodobnie dwunożność nie była w pełni wykształcona – wskazują na to badania kanałów półkolistych, które u naczelnych badał Fred Spoor. Australopitek ten prawdopodobnie pędził częściowo nadrzewny tryb życia, na co wskazują m.in. odkrycia w Sterkfontein.
Synonimy
- Plesianthropus transvaalensis
- Australopithecus prometheus[1]
- Australopithecus transvaalensis
- Meganthropus africanus
- Paraustralopithecus aethiopicus
Zobacz też
Przypisy
Linki zewnętrzne
- Lista skamielin Australopithecus africanus. msu.edu. [zarchiwizowane z tego adresu (2010-12-24)]. (ang.)
Media użyte na tej stronie
Autor: (of code) -xfi-, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
The Wikispecies logo created by Zephram Stark based on a concept design by Jeremykemp.
(c) Oryctes, CC BY-SA 3.0
Cast of the Sahelanthropus tchadensis holotype cranium TM 266-01-060-1, dubbed Toumaï, in facio-lateral view.
Autor: Autor nie został podany w rozpoznawalny automatycznie sposób. Założono, że to Alberto Salguero (w oparciu o szablon praw autorskich)., Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Pablo Alberto Salguero Quiles
Autor: Thomas Roche from San Francisco, USA, Licencja: CC BY-SA 2.0
Homo erectus, Museum of Natural History, Ann Arbor, Michigan, November 2007.
Autor: High Contrast, Licencja: CC BY 3.0 de
Anthroplogy - human skull of a boy. The skull is of a boy that was likely about 8 years old. The age of the skull itself is not known. Note the mandibular central incisors breaking through.
Autor: José Braga;Didier Descouens, Licencja: CC BY-SA 4.0
Australopithecus africanus - Two views of same specimen formerly named Plesianthropus transvaalensis (holotype)
- Natural endocranial cast (485 cm3) (Sts 60), articulated with a fragmentary skull still embedded in breccia (TM 1511) wich includes the left maxilla, the orbital area and most of the skull base.
- Found by G. W. Barlow and described by Robert Broom in 1938.
- Discovered in South Africa . Collection of the Transvaal Museum, Northern Flagship Institute, Pretoria South Africa.
Autor: José Braga; Didier Descouens, Licencja: CC BY-SA 4.0
The original complete skull (without upper teeth and mandible) of a 2,1 million years old Australopithecus africanus specimen so-called "Mrs. Ples" (catalogue number STS 5, Sterkfontein cave, hominid fossil number 5), discovered in South Africa . Collection of the Transvaal Museum, Northern Flagship Institute, Pretoria, South Africa.