Cieśnina Juana de Fuca
 Widok z Cieśniny Juana de Fuca w kierunku południowym. Widoczne miasto Port Angeles i pasmo Olympic Mountains. | |
| Państwo | |
|---|---|
| Akweny • Łączy wody • Z wodami | |
| Lądy • Oddziela • Od | |
| Wymiary • długość • szerokość |
|
| Miejscowości nadbrzeżne | |
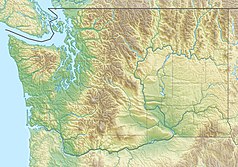
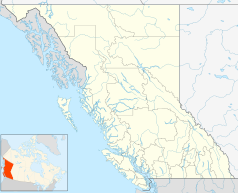
Cieśnina Juana de Fuca (ang. Strait of Juan de Fuca, Juan de Fuca Strait) – cieśnina Oceanu Spokojnego, część morza Salish[1], pomiędzy kanadyjską wyspą Vancouver (prowincja Kolumbia Brytyjska) a półwyspem Olympic (stan Waszyngton, USA)[2].
Cieśnina rozciąga się na długości 130–160 km, jej szerokość wynosi od 18 do 27 km[2]. Zachodni kraniec cieśniny, gdzie łączy się ona z otwartym oceanem, wyznaczają przylądek Flattery (Cape Flattery) na półwyspie Olympic, wyspa Tatoosh i przylądek Carmanah (Carmanah Point) na wyspie Vancouver[3]. Na wschodzie Cieśnina Juana de Fuca dociera do wysp San Juan i Whidbey, gdzie styka się z cieśniną Haro (Haro Strait), kanałem San Juan (San Juan Channel), cieśniną Rosario (Rosario Strait) i zatoką Puget (Puget Sound)[2][3]. Głębokość cieśniny wynosi od 275 m u styku z oceanem do 90 m w jej wschodniej części[2].
Główne miasta nad cieśniną to Victoria i Port Angeles. Przebiega tędy droga wodna prowadząca do portów w Vancouverze i Seattle[2].
Cieśnina nazwana została na cześć Juana de Fuca, greckiego żeglarza w służbie hiszpańskiej, który miał dotrzeć tutaj w 1592 roku[3].
Przypisy
- ↑ Salish Sea. Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). [dostęp 2016-08-21]. (ang.).
- ↑ a b c d e Juan de Fuca Strait, [w:] Encyclopædia Britannica [online] [dostęp 2016-08-21] (ang.).
- ↑ a b c Strait of Juan de Fuca. Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). [dostęp 2016-08-21]. (ang.).
Media użyte na tej stronie
Autor: Uwe Dedering, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Relief location map of the USA (without Hawaii and Alaska).
EquiDistantConicProjection : Central parallel :
* N: 37.0° N
Central meridian :
* E: 96.0° W
Standard parallels:
* 1: 32.0° N * 2: 42.0° N
Made with Natural Earth. Free vector and raster map data @ naturalearthdata.com.
Formulas for x and y:
x = 50.0 + 124.03149777329222 * ((1.9694462586094064-({{{2}}}* pi / 180))
* sin(0.6010514667026994 * ({{{3}}} + 96) * pi / 180))
y = 50.0 + 1.6155950752393982 * 124.03149777329222 * 0.02613325650382181
- 1.6155950752393982 * 124.03149777329222 *
(1.3236744353715044 - (1.9694462586094064-({{{2}}}* pi / 180))
* cos(0.6010514667026994 * ({{{3}}} + 96) * pi / 180))
Autor: Nzeemin, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Relief map of Canada.
- Projection: Lambert Conformal Conic Projection
- lon0 = -27°
- lat0 = 69°
- lat1 = 51°
- lat2 = 45°
- Projection/coords for GMT:
-Jl-95/49/49/77/1:29350000 -R-121.36/38.29/-11.5/63.0r
The flag of Navassa Island is simply the United States flag. It does not have a "local" flag or "unofficial" flag; it is an uninhabited island. The version with a profile view was based on Flags of the World and as a fictional design has no status warranting a place on any Wiki. It was made up by a random person with no connection to the island, it has never flown on the island, and it has never received any sort of recognition or validation by any authority. The person quoted on that page has no authority to bestow a flag, "unofficial" or otherwise, on the island.
Autor: Hanhil (talk) 16:54, 24 September 2009 (UTC), Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Location map of British Columbia, Canada
Autor: own work, Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Strait of Juan de Fuca with the Olympic mountains in the background, Washington, USA
Autor: Carport, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Physical location map of Washington, USA