Funkcja trójkątna
Funkcja trójkątna jest zdefiniowana jako:
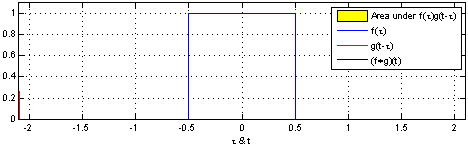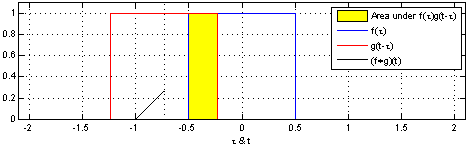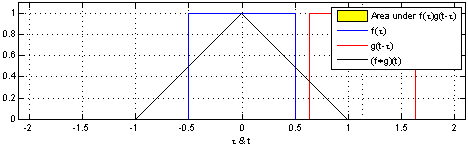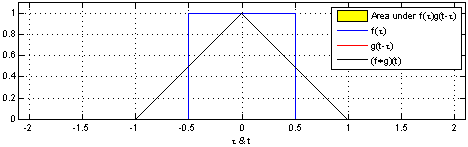
lub, co jest równoważne, jako splot dwóch identycznych jednostkowych funkcji prostokątnych:
Funkcja ta ma zastosowanie w przetwarzaniu sygnałów. Jest przykładem idealnego sygnału, którego cechy można odnaleźć w sygnałach rzeczywistych. Jednym z jej zastosowań jest Okno Trójkątne lub Okno Bartletta.
Skalowanie
Dla dowolnego parametru zachodzi:
Transformacja Fouriera
Transformatę Fouriera funkcji trójkątnej można łatwo uzyskać, korzystając z twierdzenia o splocie i transformaty funkcji prostokątnej:
Zobacz też
Media użyte na tej stronie
Autor:
- Convolution_of_box_signal_with_itself.gif: Brian Amberg
- derivative work: Tinos (talk)
An animation displaying the process and result of convolving a box signal with itself. For each position in the resulting hat function the input functions and the multiplied input functions are shown, and the area which is integrated is marked. This work mimics [1] but includes the source code and shows the result of the convolution in the same graph as the input functions.