Gązewnikowate
 Gązewnik europejski | |
| Systematyka[1][2] | |
| Domena | |
|---|---|
| Królestwo | |
| Podkrólestwo | |
| Nadgromada | |
| Gromada | |
| Podgromada | |
| Nadklasa | |
| Klasa | |
| Nadrząd | |
| Rząd | |
| Rodzina | gązewnikowate |
| Nazwa systematyczna | |
| Loranthaceae Juss. Ann. Mus. Natl. Hist. Nat. 12: 292. 1808 | |
| Zasięg występowania | |
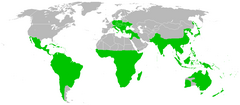 | |
Gązewnikowate (Loranthaceae) – rodzina roślin z rzędu sandałowców licząca 77 rodzajów[3] i ok. 950 gatunków. Centrum występowania przedstawicieli rodziny stanowi półkula południowa i strefa tropików. Najdalej na północ sięgają do Meksyku, Europy południowej i Japonii[1].
Charakterystyka
Przeważnie krzewinki, rzadziej rośliny zielne. Są to zielone (zawierające chlorofile) półpasożyty drzew i krzewów wrastające do ich pni ssawkami. Tylko niektóre zakorzeniają się w glebie.
- Liście
- Ulistnienie naprzeciwległe albo okółkowe. Pospolite są kandelabrowate włoski. Szparki przeważnie typu rubiaceus. Mezofil jest grzbietobrzuszny albo izobilateralny, bądź złożony z komórek izodiametrycznych.
- Kwiaty
- Zebrane w grona lub wierzchotki, często zapylane przez ptaki i owady.
- Owoc
- Jagoda lub pestkowiec.
- Cechy anatomiczne
- Perycykl zawiera izolowane grupy włókien. Szczawian wapnia: pojedyncze kryształy lub druzy.
Systematyka
W niektórych systemach klasyfikacyjnych do gązewnikowatych zaliczano jemiołowate jako podrodzinę Viscoideae[4]. Mimo pewnych podobieństw okazało się jednak, że grupy te po połączeniu nie tworzą taksonu monofiletycznego[1].
- Pozycja według Angiosperm Phylogeny Website (aktualizowany system APG IV z 2016)
| sandałowce |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Pozycja w systemie Reveala (1994-1999)
Gromada okrytonasienne (Magnoliophyta Cronquist), podgromada Magnoliophytina Frohne & U. Jensen ex Reveal, klasa Rosopsida Batsch, podklasa różowe (Rosidae Takht.), nadrząd Santalanae Thorne ex Reveal, rząd sandałowce (Santalales Dumort.), podrząd Loranthineae Engl., rodzina gązewnikowate (Loranthaceae Juss.)[5].
- Wykaz rodzajów[3]
- Actinanthella Balle
- Aetanthus (Eichler) Engl.
- Agelanthus Tiegh.
- Alepis Tiegh.
- Amyema Tiegh.
- Amylotheca Tiegh.
- Atkinsonia F.Muell.
- Bakerella Tiegh.
- Barathranthus (Korth.) Miq.
- Benthamina Tiegh.
- Berhautia Balle
- Cecarria Barlow
- Cladocolea Tiegh.
- Cyne Danser
- Dactyliophora Tiegh.
- Decaisnina Tiegh.
- Dendropemon (Blume) Rchb.
- Dendrophthoe Mart.
- Desmaria Tiegh.
- Diplatia Tiegh.
- Distrianthes Danser
- Elytranthe (Blume) Blume
- Emelianthe Danser
- Englerina Tiegh.
- Erianthemum Tiegh.
- Gaiadendron G.Don
- Globimetula Tiegh.
- Helicanthes Danser
- Helixanthera Lour.
- Ileostylus Tiegh.
- Ixocactus Rizzini
- Kingella Tiegh.
- Lampas Danser
- Lepeostegeres Blume
- Lepidaria Tiegh.
- Ligaria Tiegh.
- Loranthus Jacq. – gązewnik
- Loxanthera (Blume) Blume
- Lysiana Tiegh.
- Macrosolen (Blume) Rchb.
- Moquiniella Balle
- Muellerina Tiegh.
- Notanthera (DC.) G.Don
- Nuytsia R.Br. ex G.Don – nujcja
- Oedina Tiegh.
- Oliverella Tiegh.
- Oncella Tiegh.
- Oncocalyx Tiegh.
- Oryctanthus (Griseb.) Eichler
- Oryctina Tiegh.
- Panamanthus Kuijt
- Papuanthes Danser
- Pedistylis Wiens
- Peraxilla Tiegh.
- Phragmanthera Tiegh.
- Phthirusa Mart.
- Plicosepalus Tiegh.
- Psathyranthus Ule
- Psittacanthus Mart.
- Rhizomonanthes Danser
- Scurrula L.
- Septulina Tiegh.
- Socratina Balle
- Sogerianthe Danser
- Spragueanella Balle
- Struthanthus Mart.
- Tapinanthus (Blume) Blume
- Taxillus Tiegh.
- Tetradyas Danser
- Thaumasianthes Danser
- Tolypanthus (Blume) Blume
- Trilepidea Tiegh.
- Tripodanthus (Eichler) Tiegh.
- Tristerix Mart.
- Trithecanthera Tiegh.
- Tupeia Cham. & Schltdl.
- Vanwykia Wiens
Przypisy
- ↑ a b c Peter F. Stevens, Angiosperm Phylogeny Website, Missouri Botanical Garden, 2001– [dostęp 2021-03-08] (ang.).
- ↑ Michael A. Ruggiero i inni, A Higher Level Classification of All Living Organisms, „PLOS One”, 10 (4), 2015, art. nr e0119248, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119248, PMID: 25923521, PMCID: PMC4418965 [dostęp 2021-03-08] (ang.).
- ↑ a b Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew: List of genera in family Loranthaceae (ang.). Vascular Plant Families and Genera. [dostęp 2014-04-11].
- ↑ Wielka Encyklopedia Przyrody. Rośliny kwiatowe. Warszawa: Muza SA, 1998. ISBN 83-7079-778-4.
- ↑ Crescent Bloom: Loranthaceae (ang.). The Compleat Botanica. [dostęp 2009-07-22].
Media użyte na tej stronie
(c) Photographs by Gnangarra...commons.wikimedia.org, CC BY 2.5 au
Perth
The Western Australian Christmas tree (Nuytsia floribunda) is a parasitic tree found in Western Australia. It is known for its bright yellow flowers around Christmas time (summer). It can grow to 10m tall. It is a member of the Loranthaceae or mistletoe family.Autor: JMK, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Flowers of the semi-parasitic Red mistletoe growing in Faurea saligna in the Waterberg, South Africa. A few flowers have opened at top left. The other tree species parasitized locally is Protea caffra, also Proteaceae, while other trees are unaffected.
FloraWeb.de: Eichenmistel, Loranthus europaeus Jacq.
- Original Caption
- Eichen-Mistel, Loranthus europaeus





