Księstwo Lippe
| 1123–1918 | |||||
| |||||
 | |||||
| Stolica | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ustrój polityczny | |||||
| Data powstania | |||||
| Zlikwidowane w wyniku | |||||
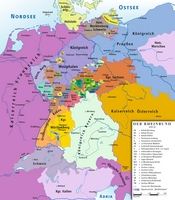
Hrabstwo Lippe (od 1613 Lippe-Detmold), od 1789 Księstwo Lippe – historyczne państwo w dzisiejszych Niemczech. Kraj Świętego Cesarstwa Rzymskiego. Od 1815 roku państwo Związku Niemieckiego. Od 1871 kraj Cesarstwa Niemieckiego.
Było ono położone pomiędzy Wezerą oraz południowo-wschodnią częścią Lasów Teutoburskich.
Historia
Pierwszym władcą Lippe był Bernhard I, który, otrzymując w 1123 od cesarza rzymsko-niemieckiego Lotara III, został panem Lippe. Następcy Bernharda odziedziczyli lub zdobyli kilka krajów w Rzeszy. Szymon V był pierwszym władcą tytułującym się hrabią.
Po śmierci hrabiego Szymona VI w 1613, Lippe zostało podzielone na trzy kraje. Lippe-Detmold zostało dane Szymonowi VII, Lippe-Brake hrabiemu Ottonowi, natomiast Lippe-Alverdissen przeszło w ręce hrabiego Filipa. Hrabstwo Lippe-Brake zostało połączone pod władzą głównej linii z Detmold w 1709. Inna gałąź boczna rodziny została utworzona przez hrabię Jana Hermana, syna Szymona VII, który był założycielem linii Lippe-Biesterfeld.
W 1789 hrabiom Lippe-Detmold nadany został tytuł książęcy. Od tamtego momentu nie stosowano już członu Detmold w nazwie księstwa.
Krótko po włączeniu w skład Cesarstwa Niemieckiego w 1871, linia Lippe-Detmold wygasła w 1895. Spowodowało to spór o dziedziczenie Lippe-Detmold pomiędzy sąsiadującym księstwem Schaumburg-Lippe oraz linią Lippe-Biesterfeld. Spór został rozwiązany przez sąd cesarski w Lipsku w 1905, kiedy ziemie dostały się w ręce linii Lippe-Biesterfeld, która wcześniej nie miała żadnej ziemi.
Księstwo Lippe przestało istnieć 12 listopada 1918 roku, wraz z abdykacją księcia Leopolda IV oraz utworzeniem Wolnego Państwa Lippe.
Władcy
Książęta
- 1789–1802 Leopold I
- 1802–1851 Leopold II
- 1851–1875 Leopold III
- 1875–1895 Waldemar
- 1895–1905 Aleksander
- 1905–1918 Leopold IV
Tytularni książęta Lippe
- 1918–1949 Leopold IV
- 1949–2015 Armin (1924–2015)
- od 2015 Stefan (ur. 1959)
Przypisy
Media użyte na tej stronie
Flaga Niemiec o proporcjach 3:2
Flag of the duchy of Saxe-Coburg & Gotha 1911-1920; Ratio (2:3)
Flag of the Kingdom of Württemberg; Ratio (3:5)
Autor: ziegelbrenner, Licencja: CC BY 2.5
Map of Confederation of the Rhine 1812
Flag of the Grand Duchy of Baden 1855-1891; Ratio (3:5)
Flag of the duchy of Saxe-Coburg & Gotha 1826-1911; Ratio (2:3)
Flag of Alsace-Lorraine, adopted on the 25th of June 1912 and flag of the Republic of Alsace-Lorraine (Nov 11 1918 - Nov 21 1918)
Flag of the Duchy of Anhalt and also flag of Augsburg
Flag of the principality of Reuß Younger Line; Ratio (4:5) may also be (5:6)
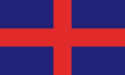
Flag of the principality of Lippe; Ratio (2:3)
Flag of the Grand Duchies of Mecklenburg-Strelitz and Mecklenburg-Schwerin; Ratio (2:3)
Autor: Glasshouse, Licencja: CC BY-SA 4.0
Coat of Arms of the Principality of Lippe
Autor: User:52 Pickup, Licencja: CC BY-SA 2.5
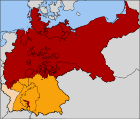
The North German Confederation / Norddeutscher Bund (1867–1871) in red. The states that would join the confederation and form the German Empire are in orange. Alsace-Lorraine, the territory annexed from France following the Franco-Prussian War of 1871, is in a paler orange.
Autor: Milenioscuro, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Locator map of Lippe in the German Empire
Flag of the Grand Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach 1813-1897; Ratio (2:3)
Flag of the principalities of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen and Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt; Ratio (2:3)
Flag of the Kingdom of Saxony; Ratio (2:3)
Flag of the Grand Duchy of Hesse without arms; Ratio (4:5)
Civil flag of Oldenburg, before 1871 and beween 1921 and 1935
Flag of the principality of Schaumburg-Lippe; Ratio (2:3), c. 1880–1935
Flag of the duchy of Brunswick; Ratio (2:3)
Imperial Eagle of the German Empire from 1889 to 1918.
Flag of the principality of Reuss Elder Line; Ratio (27:34)