Lista kodów krajowych MKOl-u
Lista kodów MKOl-u zawiera 241 pozycji, z których obecnie używanych jest 204. Międzynarodowy Komitet Olimpijski używa dla każdego krajowego komitetu olimpijskiego jednego trzyliterowego skrótu.
Niektóre ze skrótów MKOl-u nie odpowiadają kodom według normy międzynarodowej ISO3166-1 alpha-3. Skróty Międzynarodowego Komitetu Olimpijskiego nie są wiążące dla innych międzynarodowych organizacji sportowych. Tak na przykład w Commonwealth Games czy na zawodach FIFA, FINA lub IAAF dla niektórych drużyn stosuje się inne skróty niż w igrzyskach olimpijskich.
Historia
W czasie zimowych igrzysk olimpijskich w 1956 roku i letnich igrzysk w 1960 roku po raz pierwszy użyto w oficjalnych raportach dla krajowych drużyn olimpijskich czy drużyn trzyliterowych kodów. Początkowo skróty były oparte na języku danego gospodarza igrzysk (np. GIA dla Japonii od włoskiej nazwy Japonii Giappone, ponieważ zarówno zimowe igrzyska olimpijskie w 1956 roku, jak i letnie igrzyska w 1960 roku odbywały się we Włoszech) lub pochodziły od francuskiej nazwy danego kraju (np. COR dla Korei, po francusku Corée).
Do zimowych igrzysk olimpijskich w 1972 roku większość kodów była zestandaryzowana. Niemniej jednak zdarzały się pewne zmiany w następnych latach. Zmiany polityczne, jak na przykład rozpad Związku Radzieckiego czy Jugosławii, połączenie NRD i RFN powodowały wprowadzanie nowych oznaczeń.
Kody
Poniżej znajdują się kody reprezentacji olimpijskich, które były kiedykolwiek używane przez Międzynarodowy Komitet Olimpijski lub występowały w oficjalnych raportach olimpijskich.
Tłustym drukiem podano oznaczenia, obecnie używane w zestawieniach MKOl-u. Kody na jasnych polach są przyporządkowane do historycznych – nieistniejących już krajowych komitetów olimpijskich lub reprezentacji. Kursywą umieszczono oznaczenia używane wcześniej, które wyszły z użycia.
| Kod | Drużyna | od | do | Skrót używany w oficjalnym raporcie danych igrzysk olimpijskich | Uwagi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
A | |||||
| AFG | 1936 | ||||
| AHO | 1952 | 2010 | ATO (1960) NAN (1964) | Państwo przestało istnieć 10.10.2010 i nie jest już członkiem MKOl-u. | |
| ALB | 1972 | ||||
| ALG | 1964 | AGR (1964) AGL (1968) | |||
| AND | 1976 | ||||
| ANG | 1980 | ||||
| ANT | 1964 | ||||
| ANZ | 1908 | 1912 | wspólna reprezentacja AUS i NZL | ||
| ARG | 1920 | ||||
| ARM | 1994 | 1900–1912 – część RUS 1924–1988 – część URS 1992 – część EUN | |||
| ARU | 1988 | ||||
| ASA | 1988 | ||||
| AUS | 1896 | 1908–1912 – część ANZ | |||
| AUT | 1896 | ||||
| AZE | 1994 | 1900–1912 – część RUS 1924–1988 – część URS 1992 – część EUN | |||
B | |||||
| BAH | 1952 | ||||
| BAN | 1984 | ||||
| BAR | 1968 | BAD (1964) | 1960 – część BWI | ||
| BDI | 1996 | ||||
| BEL | 1900 | ||||
| BEN | 1980 | 1972–1976 – start jako DAH | |||
| BER | 1936 | ||||
| BHU | 1984 | ||||
| BIH | 1992 | BSH (1992 L) | 1920–1988 – część YUG | ||
| BIR | 1948 | 1988 | BUR (1964) | Startuje obecnie jako MYA. | |
| BIZ | 1976 | 1968–1972 – start jako HBR | |||
| BLR | 1994 | 1900–1912 – część RUS 1924–1988 – część URS 1992 – część EUN | |||
| BOH | 1900 | 1912 | Była częścią Austro-Węgier, wystawiła jednak własną reprezentację na igrzyska olimpijskie. Po I wojnie światowej Czechy, wraz z innymi terenami jako Czechosłowacja (ze skrótem TCH). Startuje obecnie jako CZE. | ||
| BOL | 1936 | ||||
| BOR | 1956 | 1960 | Od 1963 część Malezji, startuje obecnie jako MAS. | ||
| BOT | 1980 | ||||
| BRA | 1920 | ||||
| BRN | 1984 | ||||
| BRU | 1988 | ||||
| BUL | 1896 | ||||
| BUR | 1988 | 1972–1984 – start jako VOL | |||
| BWI | 1960 | ANT (1960) | wspólna drużyna BAR, JAM i TRI | ||
C | |||||
| CAF | 1968 | AFC (1968) | |||
| CAM | 1956 | CAB (1964) | 1972–1976 – start jako KHM | ||
| CAN | 1900 | ||||
| CAY | 1976 | ||||
| CEY | 1948 | 1972 | Startuje obecnie jako SRI. | ||
| CGO | 1972 | 1968 – start jako COB | |||
| CHA | 1964 | CHD (1964) | |||
| CHI | 1896 | CIL (1956 Z, 1960 L) | |||
| CHN | 1932 | 1932–1956 – skrót używany dla Republiki Chińskiej (startowała następnie jako ROC) od 1984 – używany jako skrót dla Chińskiej Republiki Ludowej | |||
| CIV | 1964 | IVC (1964), CML (1968) | |||
| CMR | 1964 | ||||
| COB | 1964 | Obecnie startuje jako CGO. | |||
| COD | 1968 | 1968–1980 – start jako COK 1984–1996 – start jako ZAI | |||
| COK | 1988 | 1968–1980 – skrót używany dla Konga-Kinszazy od 1988 – skrót używany dla Wysp Kokosowych | |||
| COK | 1968 | 1980 | Startuje obecnie jako COD. | ||
| COL | 1932 | ||||
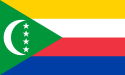
| COM | 1996 | ||||
| CPV | 1996 | ||||
| CRC | 1936 | COS (1964), CTC (1984 Z) | |||
| CRO | 1992 | 1920–1988 – część YUG | |||
| CUB | 1900 | ||||
| CYP | 1980 | ||||
| CZE | 1994 | 1900–1912 – start jako BOH 1920–1992 – część TCH | |||
D | |||||
| DAH | 1964 | 1976 | DAY (1964) | Startuje obecnie jako BEN. | |
| DEN | 1896 | DAN (1960 L, 1968 Z), DIN (1968 L) | |||
| DJI | 1984 | ||||
| DMA | 1996 | ||||
| DOM | 1964 | ||||
E | |||||
| ECU | 1924 | ||||
| EGY | 1912 | 1960–1968 – start jako UAR | |||
| ERI | 2000 | ||||
| ESA | 1964 | SAL (1964–1976) | |||
| ESP | 1900 | SPA (1956–1964, 1968 Z) | |||
| EST | 1924 | 1900–1912 – część RUS 1948–1988 – część URS | |||
| ETH | 1956 | ETI (1960, 1968) | |||
| EUA | 1956 1960 | 1956 1964 | GER (1956–1964) | MKOl wprowadził ten skrót dopiero po zjednoczeniu Niemiec dla oddania specyficznej sytuacji politycznej. Członkowie wspólnej drużyny olimpijskiej byli wyłaniani spośród sportowców z Republiki Federalnej Niemiec i Niemieckiej Republiki Demokratycznej. Po tym jak NRD została oficjalnie uznana przez MKOl 6 października 1965, sportowcy startowali w osobnych drużynach: FRG i GDR | |
| EUN | 1992 | następcy: ARM, AZE, BLR, GEO, KAZ, KGZ, MDA, RUS, TJK, TKM, UKR i UZB | |||
F | |||||
| FIJ | 1956 | FIG (1960) | |||
| FIN | 1908 | Finlandia po raz pierwszy brała udział w letnich igrzyskach olimpijskich w 1908 roku w Londynie. Wtedy i w następnych letnich igrzyskach w 1912 roku Finlandia była autonomicznym księstwem Rosji. Wyniki zawodników fińskich były traktowane oddzielnie w stosunku do rosyjskich. Od 1920 roku Finlandia bierze udział w igrzyskach olimpijskich jako samodzielne państwo. | |||
| FRA | 1896 | ||||
| FRG | 1968 | 1988 | ALL (1968 Z), ALE (1968 L), GER (1972–1976) | Po zjednoczeniu Niemiec – GER. | |
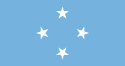
| FSM | 2000 | ||||
G | |||||
| GAB | 1972 | ||||
| GAM | 1984 | ||||
| GBR | 1896 | GRB (1956 W–1960), GBI (1964) | |||
| GBS | 1996 | ||||
| GDR | 1968 | 1988 | ADE (1968) | Po zjednoczeniu Niemiec – GER | |
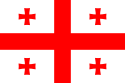
| GEO | 1996 | 1900–1912 – część RUS 1924–1988 – część URS 1992 – część EUN | |||
| GEQ | 1984 | ||||
| GER | 1896 1952 1992 | 1936 1952 | ALL (1968 Z), ALE (1968 L), FRG (1980–1988) | 1956–1964 – start jako GER, przez MKOl obecnie podawane jako EUA 1968–1988 – udział jako osobne reprezentacje FRG i GDR | |
| GHA | 1960 | ||||
| GRE | 1896 | ||||
| GRN | 1984 | ||||
| GUA | 1952 | GUT (1964) | |||
| GUI | 1968 | ||||
| GUI | 1948 | 1964 | GUA (1960) | od 1968 jako Gujana | |
| GUM | 1988 | ||||
| GUY | 1948 | ||||
H | |||||
| HAI | 1924 | ||||
| HBR | 1968 | 1972 | Startuje obecnie jako BIZ. | ||
| HKG | 1952 | HOK (1960–1968) | |||
| HON | 1968 | ||||
| HUN | 1896 | UNG (1956 Z, 1960 L) | 1896–1920 – część Austro-Węgier | ||
I | |||||
| IHO | 1952 | Startuje obecnie jako INA. | |||
| INA | 1952 | INS (1960) | 1952 – start jako IHO | ||
| IND | 1900 | ||||
| IOA | 2000 | 2012 | Używany:
| ||
| IOP | 1992 | Używany, gdy Serbia i Czarnogóra nie były jeszcze uznane. Ten skrót może znaleźć zastosowanie w przyszłości w podobnych sytuacjach. | |||
| IRI | 1948 | IRN (1948–1988), IRA (1968 Z) | |||
| IRL | 1924 | 1896–1920 – część GBR | |||
| IRQ | 1948 | IRK (1960, 1968) | |||
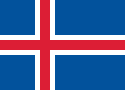
| ISL | 1908 | ICE (1960 Z, 1964 L) | |||
| ISR | 1952 | ||||
| ISV | 1968 | ||||
| ITA | 1900 | ||||
| IVB | 1984 | ||||
J | |||||
| JAM | 1948 | 1960 – część BWI | |||
| JOR | 1968 | ||||
| JPN | 1912 | GIA (1956 Z, 1960 L), JAP (1960 Z) | |||
K | |||||
| KAZ | 1994 | 1900–1912 – część RUS 1924–1988 – część URS 1992 – część EUN | |||
| KEN | 1956 | ||||
| KGZ | 1994 | 1900–1912 – część RUS 1924–1988 – część URS 1992 – część EUN | |||
| KHM | 1972 | 1976 | Startuje obecnie jako CAM. | ||
| KIR | 2004 | ||||
| KOR | 1948 | COR (1956 Z, 1960 L, 1968 L, 1972 L) | |||
| KOS | 2014 | ||||
| KSA | 1988 | ARS (1968–1976), SAU (1980–1984) | |||
| KUW | 1968 | ||||
L | |||||
| LAO | 1980 | ||||
| LAT | 1924 | 1900–1912 – część RUS 1948–1988 – część URS | |||
| LBA | 1964 | LYA (1964), LBY (1968 Z) | |||
| LBR | 1956 | ||||
| LCA | 1996 | ||||
| LES | 1972 | ||||
| LIB | 1948 | LEB (1960 Z, 1964 L) | |||
| LIE | 1936 | LIC (1956 Z, 1964 L, 1968 Z) | |||
| LTU | 1924 | LIT (1992 Z) | 1900–1912 – część RUS 1948–1988 – część URS | ||
| LUX | 1908 | ||||
M | |||||
| MAD | 1964 | MAG (1964) | |||
| MAL | 1956 | 1960 | Startuje obecnie jako MAS. | ||
| MAR | 1960 | MRC (1964) | |||
| MAS | 1956 | 1956–1960 – start jako MAL | |||
| MAW | 1972 | ||||
| MDA | 1994 | MLD (1994) | 1900–1912 – część RUS 1920–1936 – część ROM 1952–1988 – część URS 1992 – część EUN | ||
| MDV | 1988 | ||||
| MEX | 1924 | ||||
| MGL | 1964 | MON (1968 Z) | |||
| MHL | 2008 | ||||
| MKD | 1996 | 1920–1988 – część YUG 1992 – start jako IOP | |||
| MLI | 1964 | ||||
| MLT | 1928 | MAT (1960–1964) | |||
| MNE | 2008 | 1920–1988 – część YUG 1992 – start jako IOP 1996-2002 – część YUG 2004-2006 – część SCG 2008 – start jako MNE | |||
| MON | 1920 | ||||
| MOZ | 1980 | ||||
| MRI | 1984 | ||||
| MTN | 1984 | ||||
| MYA | 1992 | 1948–1988 – start jako BIR | |||
N | |||||
| NAM | 1992 | ||||
| NCA | 1968 | NCG (1964), NIC (1968) | |||
| NED | 1900 | OLA (1956 Z), NET (1960 Z), PBA (1960 L), NLD (1964 L), HOL (1968–1988) | |||
| NEP | 1964 | ||||
| NGR | 1952 | NGA (1964) | |||
| NIG | 1968 | NGR (1964) | |||
| NOR | 1900 | ||||
| NRU | 1996 | ||||
| NZL | 1920 | NZE (1960, 1968 Z) | 1908–1912 – część ANZ | ||
O | |||||
| OMA | 1984 | ||||
| OAR | 2018 | Używany dla Olimpijczyków z Rosji, którzy występują pod neutralną flagą po decyzji MKOl-u o wykluczeniu Rosji z zimowych igrzysk olimpijskich w Pjongczangu[1]. | |||
P | |||||
| PAK | 1948 | ||||
| PAN | 1928 | ||||
| PAR | 1964 | ||||
| PER | 1936 | ||||
| PHI | 1924 | FIL (1960, 1968) | |||
| PLE | 1996 | ||||
| PLW | 2000 | ||||
| PNG | 1976 | NGY (1976–1980), NGU (1984–1988) | |||
| POL | 1924 | ||||
| POR | 1912 | ||||
| PRK | 1972 | NKO (1964 L, 1968 Z), CDN (1968) | |||
| PUR | 1948 | PRI (1960), PRO (1968) | |||
Q | |||||
| QAT | 1984 | ||||
R | |||||
| RHN | 1964 | Startuje obecnie jako ZAM. | |||
| RHO | 1928 | 1960 | Brytyjska kolonia została w 1963 podzielona na Rodezję Północną i Południową. Po zmianie nazwy Rodezji Północnej na Zambia skrót był dalej używany dla Rodezji Południowej. Startuje obecnie jako ZIM. | ||
| RHS | 1964 | Po zmianie nazwy Rodezji Północnej na Zambia skrót RHO był dalej używany dla Rodezji Południowej. Startuje obecnie jako ZIM. | |||
| ROC | 1968 | 1972 | RCF (1960) | Startuje obecnie jako TPE. | |
| ROU | 1924 | ROM (1956–1960, 1972–2006), RUM (1964–1968) | |||
| RSA | 1904 | 1908–1960 – start jako SAF | |||
| RUS | 1900 | 1900–1912 – start jako RUS 1952–1988 – start jako URS 1992 – część EUN od 1994 – start jako RUS | |||
| RWA | 1984 | ||||
S | |||||
| SAA | 1952 | Po II wojnie Światowej kraj Saary był do 1957 roku pod francuskim protektoratem. | |||
| SAF | 1904 | 1960 | Startuje obecnie jako RSA. | ||
| SAM | 1984 | ||||
| SCG | 2004 | 2006 | 1920–1988 – część YUG 1992 – start jako IOP 1996-2002 – start jako YUG od 2008 – start jako SRB i MNE | ||
| SEN | 1964 | SGL (1964) | |||
| SEY | 1980 | ||||
| SRB | 1912 | 1920–1988 – część YUG 1992 – start jako IOP 1996-2002 – start jako YUG od 2008 – start jako SRB | |||
| SIN | 1948 | ||||
| SKN | 1996 | ||||
| SLE | 1968 | SLA (1968) | |||
| SLO | 1992 | 1920–1988 – część YUG | |||
| SMR | 1960 | SMA (1960–1964) | |||
| SOL | 1984 | ||||
| SOM | 1972 | ||||
| SRB | 1912 | 1912 – start jako SER 1920–1988 – część YUG 1992 – start jako IOP 1996-2002 – część YUG 2004-2006 – część SCG 2008 – start jako SRB | |||
| SRI | 1976 | 1948–1972 – start jako CEY | |||
| STP | 1996 | ||||
| SUD | 1960 | ||||
| SSD | 2012 | ||||
| SUI | 1900 | SVI (1956 Z, 1960 L), SWI (1960 Z, 1964 L) | |||
| SUR | 1968 | ||||
| SVK | 1994 | 1920–1992 – część TCH | |||
| SWE | 1896 | SVE (1956 Z, 1960 L), SUE (1968 L) | |||
| SWZ | 1972 | ||||
| SYR | 1948 | 1960–1968 – start jako UAR | |||
T | |||||
| TAG | 1964 | Startuje obecnie jako TAN. | |||
| TAI | 1960 | 1964 | TWN (1964–1968) | Startuje obecnie jako TPE. | |
| TAN | 1964 | ||||
| TCH | 1920 | 1992 | po podziale Czechosłowacji dwie drużyny narodowe: CZE i SVK | ||
| TGA | 1984 | TON (1984) | |||
| THA | 1952 | TAI (1960, 1968) | |||
| TJK | 1994 | 1900–1912 – część RUS 1924–1988 – część URS 1992 – część EUN | |||
| TKM | 1994 | 1900–1912 – część RUS 1924–1988 – część URS 1992 – część EUN | |||
| TLS | 2004 | 2000 – start jako IOA | |||
| TOG | 1972 | ||||
| TPE | 1984 | 1932–1956 – start jako CHN 1960–1964 – start jako TAI 1968–1972 – start jako ROC | |||
| TRI | 1948 | TRT (1964–1968) | 1960 – część BWI | ||
| TUN | 1960 | ||||
| TUR | 1908 | ||||
U | |||||
| UAE | 1984 | ||||
| UAR | 1960 | 1968 | RAU (1960, 1968) | Startuje obecnie jako EGY. | |
| UGA | 1956 | ||||
| UKR | 1994 | 1900–1912 – część RUS 1924–1988 – część URS 1992 – część EUN | |||
| URU | 1924 | URG (1968) | |||
| URS | 1952 1956 1984 | 1952 1980 1988 | później samodzielne reprezentacje: ARM, AZE, BLR, EST, EUN, GEO, KAZ, KGZ, LAT, LTU, MDA, RUS, TJK, TKM, UKR i UZB | ||
| USA | 1896 | SUA (1960 L), EUA (1968 L) | |||
| UZB | 1994 | 1900–1912 – część RUS 1924–1988 – część URS 1992 – część EUN | |||
V | |||||
| VAN | 1988 | ||||
| VEN | 1948 | ||||
| VIE | 1952 | VET (1964), VNM (1968–1976) | 1956–1972 – używany dla Wietnamu Południowego. Wietnam Północny nie brał udziału w igrzyskach. | ||
| VIN | 1988 | ||||
| VOL | 1972 | 1984 | Startuje obecnie jako BUR. | ||
X | |||||
| XXZ | 1896 | 1904 | Określenie drużyn składających się z zawodników pochodzących z różnych krajów. Ten skrót prawdopodobnie w przyszłości nie będzie używany, ponieważ zawodnicy są zorganizowani w ramach krajowych komitetów olimpijskich. | ||
Y | |||||
| YAR | 1984 | 1988 | Po połączeniu obu części Jemenu, reprezentacja startowała pod skrótem YEM. | ||
| YEM | 1992 | 1988 – start jako YAR 1988 – start jako YMD | |||
| YMD | 1988 | Po połączeniu obu części Jemenu, reprezentacja startowała pod skrótem YEM. | |||
| YUG | 1920 | 2002 | Później samodzielne reprezentacje: BIH, CRO, MKD, MNE, SCG, SLO i SRB | ||
Z | |||||
| ZAI | 1968 | 1996 | Startuje obecnie jako COD. | ||
| ZAM | 1968 | 1928–1960 – część RHO 1964 – start jako RHN | |||
| ZIM | 1980 | 1928–1960 – część RHO 1964 – start jako RHS | |||
Zobacz też
- Lista kodów krajowych używanych w sporcie
- Oznaczenia ISAF
Przypisy
- ↑ Pjongczang. Rosja wyrzucona z zimowych igrzysk, www.sport.pl [dostęp 2017-12-07] (pol.).
Bibliografia
- Międzynarodowy Komitet Olimpijski
- Oficjalne wyniki igrzysk olimpijskich
- Krajowe komitety olimpijskie
- Skróty nazw drużyn olimpijskich. unc.edu. [zarchiwizowane z tego adresu (2018-04-18)].
Media użyte na tej stronie
Flag of Albania
The flag of Aruba
The proportions of this flag are 3:2; however, there is no official definition for the correct proportions and also 5:3 is widely used.
Łatwo można dodać ramkę naokoło tej grafiki
Flag of the Ivory Coast, written by Jon Harald Søby, modified by Zscout370. The colors match to what is reported at http://fotw.vexillum.com/flags/ci.html.
The national flag of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Created according to the 2006 constitution : Son emblème est le drapeau bleu ciel, orné d’une étoile jaune dans le coin supérieur gauche et traversé en biais d’une bande rouge finement encadrée de jaune. (Its symbol is a sky blue flag, decorated with a yellow star in the upper left corner and crossed in the diagonal by a red strip with thin yellow borders) It seems to be identical, except for a lighter field hue, to the 1966–1971 flag.
Łatwo można dodać ramkę naokoło tej grafiki
Autor: See File history below for details., Licencja: CC0
The Flag of Dominica.
The flag of the Dominican Republic has a centered white cross that extends to the edges. This emblem is similar to the flag design and shows a bible, a cross of gold and 6 Dominican flags. There are branches of olive and palm around the shield and above on the ribbon is the motto "Dios,Patria!, Libertad" ("God, Country, Freedom") and to amiable freedom. The blue is said to stand for liberty, red for the fire and blood of the independence struggle and the white cross symbolized that God has not forgotten his people. "Republica Dominicana". The Dominican flag was designed by Juan Pablo Duarte, father of the national Independence of Dominican Republic. The first dominican flag was sewn by a young lady named Concepción Bona, who lived across the street of El Baluarte, monument where the patriots gathered to fight for the independence, the night of February 27th, 1844. Concepción Bona was helped by her first cousin María de Jesús Pina.
Made by author of Xramp, first uploaded by Denelson83 as Flag of Ecuador.svg, modifications by Husunqu.
Autor: Pedro A. Gracia Fajardo, escudo de Manual de Imagen Institucional de la Administración General del Estado, Licencja: CC0
Flaga Hiszpanii
Flag of Ethiopia
Olympic Movement flag
Proportions 2:3, created 1913, adopted 1914, first used 1920.
- Colors as per http://fairspielen.de/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/Annexe-3-Olympism_and_the_Olympic_Symbol_-_Principles_and_Usages_Guide-1.pdf
- blue: PMS 3005C
- yellow: PMS 137C
- black: PMS 426C
- green: PMS 355C
- red: PMS 192C
- Dimensions of the rings taken from http://fairspielen.de/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/Annexe-3-Olympism_and_the_Olympic_Symbol_-_Principles_and_Usages_Guide-1.pdf
Flaga Finlandii
The flag of Guam, courtesy an e-mail from the author of xrmap. Modifications by Denelson83.
The national and official state flag of Haiti; arms obtained from http://www.webchantier.com/. The civil flag can be found at here.
bendera Indonesia
The Flag of India. The colours are saffron, white and green. The navy blue wheel in the center of the flag has a diameter approximately the width of the white band and is called Ashoka's Dharma Chakra, with 24 spokes (after Ashoka, the Great). Each spoke depicts one hour of the day, portraying the prevalence of righteousness all 24 hours of it.
Flag of Israel. Shows a Magen David (“Shield of David”) between two stripes. The Shield of David is a traditional Jewish symbol. The stripes symbolize a Jewish prayer shawl (tallit).
Flag of Jamaica. “The sunshine, the land is green, and the people are strong and bold” is the symbolism of the colours of the flag. GOLD represents the natural wealth and beauty of sunlight; GREEN represents hope and agricultural resources; BLACK represents the strength and creativity of the people. The original symbolism, however, was "Hardships there are, but the land is green, and the sun shineth", where BLACK represented the hardships being faced.
Flag of Laos
Flag of Liechtenstein
Flag of Maldives. The colours used are Pantone 186 C for red and Pantone 348 C for green.
Flag of Mauritania, adopted in 2017. The National Assembly added red stripes to the top and bottom edges to represent “the blood shed by the martyrs of independence”.
Flag of Namibia
Please do not replace the simplified code by a version created with Inkscape or another vector graphics editor❗
The national flag of Nauru. Official Pantone colours are: PMS 280 blue, PMS 123 yellow.
Flag of New Zealand. Specification: http://www.mch.govt.nz/nzflag/description.html , quoting New Zealand Gazette, 27 June 1902.
Flag of Portugal, created by Columbano Bordalo Pinheiro (1857-1929), officially adopted by Portuguese government in June 30th 1911 (in use since about November 1910). Color shades matching the RGB values officially reccomended here. (PMS values should be used for direct ink or textile; CMYK for 4-color offset printing on paper; this is an image for screen display, RGB should be used.)
Flag of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland
Flag of Rwanda. The flag ratio is 2:3 with the stripes being 2:1:1. Colors are the following officially: Pantone 299 C 2X (blue), RAL 6029 (green), RAL 1023 (yellow) and RAL 1003 (golden yellow). (As of 03/08/2010, the only color used is the Pantone 299 C, which is from here. The rest of the colors are RAL shades from here.)
Flag of South Africa, also known as the Oranje-Blanje-Blou, used from 31 maja 1928 until 27 kwietnia 1994
Flag of Serbia and Montenegro, was adopted on 27 April 1992, as flag of Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1992-2003).
Flag of Serbia and Montenegro, was adopted on 27 April 1992, as flag of Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1992-2003).
Flag of Senegal
Autor: Guilherme Paula, Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
State flag of Serbia (1882-1918)
Flag of São Tomé and Príncipe
Flag of South Sudan (originally of the Sudan People's Liberation Army/Movement)
Łatwo można dodać ramkę naokoło tej grafiki
The national flag of Kingdom of Thailand since September 2017; there are total of 3 colours:
- Red represents the blood spilt to protect Thailand’s independence and often more simply described as representing the nation.
- White represents the religion of Buddhism, the predominant religion of the nation
- Blue represents the monarchy of the nation, which is recognised as the centre of Thai hearts.
Official flag used by the Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) to represent Chinese Taipei in association football matches. Also used at the Olympics from 1986 to 2010.
The flag of Navassa Island is simply the United States flag. It does not have a "local" flag or "unofficial" flag; it is an uninhabited island. The version with a profile view was based on Flags of the World and as a fictional design has no status warranting a place on any Wiki. It was made up by a random person with no connection to the island, it has never flown on the island, and it has never received any sort of recognition or validation by any authority. The person quoted on that page has no authority to bestow a flag, "unofficial" or otherwise, on the island.
Flag of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1946-1992).
The design (blazon) is defined in Article 4 of the Constitution for the Republic of Yugoslavia (1946). [1]
Flag of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1946-1992).
The design (blazon) is defined in Article 4 of the Constitution for the Republic of Yugoslavia (1946). [1]
Olympic Rings without "rims" (gaps between the rings), As used, eg. in the logos of the 2008 and 2016 Olympics. The colour scheme applied here pertains to the 2016 Olympics in Rio de Janeiro.
Olympic Rings without "rims" (gaps between the rings), As used, eg. in the logos of the 2008 and 2016 Olympics. The colour scheme applied here pertains to the 2016 Olympics in Rio de Janeiro.
Autor: Heraldry, Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Flag of British Honduras
Federal flag of the West Indies Federation, 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962
Autor: Autor nie został podany w rozpoznawalny automatycznie sposób. Założono, że to Nightstallion (w oparciu o szablon praw autorskich)., Licencja: CC BY-SA 2.5
Flag of the Federation of Malaya.
This flag should not be confused with the flag of Malaysia. The flag of Malaya has 11 stripes and 11 spokes in the star. The flag of Malaysia has 14 stripes and 14 spokes.
Autor: Simitukidia and Lokal Profil, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Flag of Fiji from 1924 to 1970
Flaga Wietnamu Południowego
Autor: Guilherme Paula, Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
State flag of Serbia (1882-1918)
Flag of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland
Olympic Movement flag
Proportions 2:3, created 1913, adopted 1914, first used 1920.
- Colors as per http://www.southyorkshire.nhs.uk/london2012/resources/LDN2012%20Brand%20Guidelines.pdf
- blue: PMS 3005C
- yellow: PMS 137C
- black: PMS 426C
- green: PMS 355C
- red: PMS 192C
- Dimensions of the rings taken from http://www.southyorkshire.nhs.uk/london2012/resources/LDN2012%20Brand%20Guidelines.pdf
Flag of Serbia and Montenegro, was adopted on 27 April 1992, as flag of Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1992-2003).
Flag of Southern Rhodesia (1964–1965) and Rhodesia (1965–1968)
Flag of the unified Team of Germany for the Olympic Games, 1960–1968.
Autor: Mysid, Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Flag of the Republic of Tanganyika
Flag of Northern Rhodesia, 1939–1964
Sable six palets wavy Argent on a Chief Azure an eagle reguardant wings expanded Or holding in the talons a Fish of the second.
Flag used in 1908–12 Olympic games to represent Australasian team
Autor: Sodacan, Licencja: CC BY-SA 4.0
Flag of British Guiana (1955–1966)