Lista największych państw w historii
Lista największych państw w historii – największe terytorialnie imperia i państwa jakie istniały na przestrzeni dziejów.
Polska (I Rzeczypospolita) w latach 1618–1621 zajmuje 99. miejsce w historii pod względem powierzchni.
| Imperium | Głowa państwa[a] | Powierzchnia (mln km²) | Mapa | Lata | Ludność (w milionach) | % światowej populacji w danym okresie |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Jerzy V | 35,8[1] | 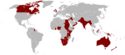 | 1922[b][2][3] | 458 (w 1938)[4] | 19.95% (458 mln na 2295 mln w 1938) | |
| Wielki Ułus Mongołów |  Kubilaj-chan | 33,0[5] |  | 1270 | 110,0 (w XIII w.) | 25,64% (110 mln na 429 mln w XIII w.) |
 Aleksander II | 23,7 |  | 1866[6] | 176,4 w 1913 | 9,84% (176,4 mln na 1791 mln w 1913) | |
| Związek Radziecki |  Michaił Kalinin[c] | 22,4 |  | 1945–1991 | 286 (1989) | 5,4% (286 mln na 5291 mln w 1989) |
 Karol IV | 20,0 |  | 1740–1790[7] | 68,2 | 12,26% (68,2 mln na 556 mln w w. XVII) | |
Władimir Putin | 17,1 |  | 2022[8] | 146,1 | 2,0% (142,9 mln na 7000 mln w 2011) | |
 Qianlong | 14,7 |  | 1790[6] | 432,2 w 1851.[e] | 36,6% (381 mln na 1.041 mln w 1820) | |
| Jazid II[9] | 13,0 | 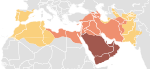 | 720–732 | 62 (w wieku VIII) | 29,5% (62 mln na 210 mln[10] w wieku VII) | |
 Alexandre Millerand | 13,5 | 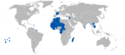 | 1923–1938[7] | 150,9 w 1938 | 6,0% (150,9 mln na 2295 mln w 1938) | |
| As-Saffah | 11,1 | 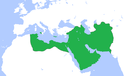 | 750 | 50 W 850 | 20,0% (50 mln na 250 mln w 850) | |
 Maria I | 10,4 |  | 1815[7] | |||
 Karol III | 10 |  | 2005[f][11] | 33,5 | 0,5% (33,5 mln[12] na 7000 mln w 2011) | |
 Xi Jinping | 9,9 |  | od 1999[h] | 1347 | 19,2% (1347 mln na 7000 mln w 2011) | |
 William McKinley | 9,8 |  | 1898–1946[i] | 141,4 w 1946 | 5,23% (141,4 mln na 2700 mln w 1950) | |
 Piotr I | 8,7 |  | 1822–1825[j] | 4 | 0,36% (4 mln na 1100 mln[13] w 1820) | |
Jerzy VI | 8,2 | (c) I, Aotearoa, CC-BY-SA-3.0 | 1939[k] | 22,3 w 2011 | 0,3% (22,3 mln na 7000 mln w 2011) | |
| Persja – Imperium Achemenidów |  Kserkses I | 8,0 |  | 480 p.n.e.[14][15] | 49,4 (w V w. p.n.e.)[16] | 44,0% (49,4 mln na 112,4 mln[17] w 480 p.n.e.) |
 Hirohito | 7,4 | 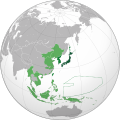 | 1942[l][7] | 134,8 w 1938 | 5,9% (134,8 mln na 2295 mln w 1938) | |
| Cesarstwo Rzymskie |  Trajan | 6,5 |  | 115–117[18] | 80,0 (w II w n.e.)[19][20] | 35,9% (80,0 mln na 223 mln[21] w II w n.e.) |
 Adolf Hitler | 6,4[m] |  | 1942 | 75,4 mln | 3,3% (75,4 mln na 2295 mln w 1938) | |
| Kaganat Turkutów | Bumyn | 6,0 |  | 557[6] | ||
 Tokta | 6,0 | 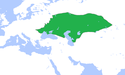 | 1310 | |||
| Królestwo Macedonii |  Aleksander Macedoński | 5,2 |  | 323 p.n.e.[6][22] | ||
 Mehmed IV | 5,2 |  | 1683[6] | 39 w XVII w. | 7,1% (39,0 mln na 556 mln w w. XVII) | |
| Kalifat Fatymidów | Al-Mu'izz | 5,1 | 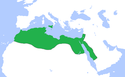 | 969[6] | ||
| Indie – Imperium Maurjów | Aśoka | 5,0 |  | 250 p.n.e[6] | 50,0 w w. II p.n.e. | 33,3% (50,0 mln na 150 mln w II w. p.n.e.[23]) |
 Augustyn I | 4.9 | © Giggette / Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 3.0 | 1822 | |||
| Imperium tybetańskie | Sadnalegs | 4,6 |  | 800[6] | ||
 Timur | 4,6 |  | 1405[6] | |||
| Indie – Imperium Wielkich Mogołów |  Aurangzeb | 4,6 |  | 1690[6] | 175 w 1700 | 29,2% (175,0 mln na 600 mln[24] w 1700) |
| Cesarstwo Bizantyńskie |  Justynian I Wielki | 4,5 |  | 550 | 35 w VI w. | 19,8% (35 mln na 177 mln[13] w 550) |
| Indie – Imperium Pala | Devapala | 4,0 | 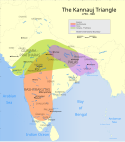 | 850 | 60 w 850 | 24,0% (60,0 mln na 250 mln w 850) |
| Państwo Heftalitów |  Toramana | 4,0 |  | 490 | ||
| Persja – Imperium Afszarydów | Nadir Szah Afszar | 4,0 |  | 1747 | ||
| Persja – Imperium Seleucydów |  Seleukos I | 3,9 |  | 301 p.n.e.[6][22] | ||
| Turcja – Wielcy Seldżucy |  Malikszah I | 3,9 | 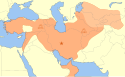 | 1080 | ||
 Wiktor Emanuel III | 3,8 |  | 1939–1940 | 51,9 w 1938 | 2,3% (51,9 mln na 2295 mln w 1938) | |
| Indie – Imperium Kuszanów | Vasudeva I | 3,8 |  | 200 | 42,37 w 140 | 19,0% (42,37 mln na 223 mln w 140) |
| Ilchanat |  Oldżajtu | 3,75 | 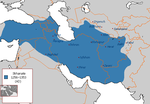 | 1310[6] | ||
 Wilhelmina | 3,7 |  | 1920–1940 | 60 w 1940 | 2,9% (60 mln na 2100 mln w 1940[13]) | |
| Indie – Imperium Ćolów | Rajadhiraja Chola | 3,6 | (c) Venu62, CC-BY-SA-3.0 | 1050[25] | ||
| Imperium Chorezmijskie | ’Ala ad-Din Muhammad II | 3,6 | 1218 | |||
| Persja – Imperium Sasanidów |  Chosrow II | 3.5 | 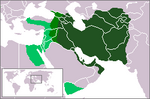 | 620[6] | 78,0 (w VII w.) | 37,1% (78,0 mln na 210 mln[10] w VII w.) |
| Indie – Imperium Guptów |  Ćandragupta II | 3,5 |  | 400[6] | 58 w 400 | 26,36% (58,0 mln na 220 mln w 400)[26] |
| Chanat Czagatajski | Czagataj | 3,5 | 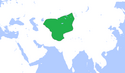 | 1310–1350[6] | ||
| Persja – Imperium Safawidów |  Isma'il I | 3,5 |  | 1512 | ||
 Wilhelm II | 3,5 |  | 1914 | 64,9 w 1914 | 3,7% 64,9 mln na 1753 mln w 1910) | |
 Andrés de Santa Cruz | 3,5 |  | 1835–1839 | |||
 Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed | 3,3 |  | od 1975[n] | 1166 | 16,7% (1166 mln na 7000 mln w 2011) | |
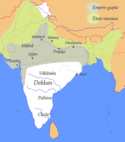
| Sułtanat Delhijski | Kutb ud-din Mubarak Szach | 3,2 | 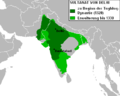 | 1320 | 70 w 1330 | 18,91% (70,0 mln na 370 mln w 1330) |
| Kaganat ujgurski | Jaγlaqar | 3,1 |  | 795[6] | ||
| Kaganat Chazarski | Zachariasz | 3,0 |  | 850[6] | ||
| Ruś Kijowska |  Jarosław I Mądry | 3,0 |  | 1050[6] | ||
| Kaganat Karachanidów | Muhammad Toghan Khan | 3,0 |  | 1025 | ||
 Chrystian VII Chrystian VII | 3,0 |  | 1800 | |||
| Imperium Medów | Kyaksares | 2,8 |  | 585 p.n.e.[6][22] | ||
| Królestwo Partów | 2,8 |  | 1[6][22] | |||
 Julio Argentino Roca | 2,8 |  | od 1881[p] | 40 | 0,6% (40 mln na 7000 mln w 2011) | |
Saladyn | 2,7 |  | 1190[6] | |||
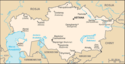
 Kasym-Żomart Tokajew | 2,7 |  | od 1991[q] | 18,4 w 2017 | 0,24% (18,4 mln na 7530 mln w 2017) | |
| Madżapahit | Hayam Wuruk | 2,7 |  | 1389 | ||
| Królestwo Indo-Greckie | 2,5 |  | 150 p.n.e. | |||
| Królestwo Greko-Baktryjskie | 2,5 | 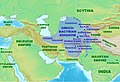 | 184 | |||
| Ramaraja | 2,5 |  | 1674–1820 | 150 w 1820 | 13,6% (150 mln na 1100 mln w 1820) | |
 Albert I | 2,5 |  | 1922–1960[r] | |||
| Chanat Kara Kitajów | Yelü Zhilugu | 2,5 |  | 1210[6] | ||
Simón Bolívar | 2,5 | 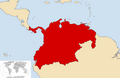 | 1825–1831 | 2,6 w 1825 | 0,23% (2,6 mln na 1100 mln w 1825) | |
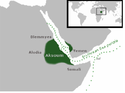
| Abdel Fattah Muhammad al-Maghrabi | 2,5 | 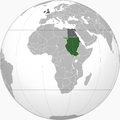 | 1956–2011[s] | 33 w 2009 | 0,5% (33 mln na 6820 mln w 2009) | |
 Ahmed Ben Bella | 2,3 |  | od 1962 | 41,3 w 2018 | 0,54% (41,3 mln na 7530 mln w 2018) | |
| Chiny – Cesarstwo Jin | Taizong | 2,3 | 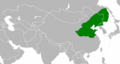 | 1126[6] | ||
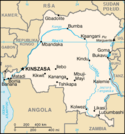
| Joseph Kasavubu | 2,3 |  | od 1963[t]- | 81,3 w 2018 | 1,1% (81,3 mln na 7530 mln w 2018) | |
 Napoleon I | 2,1[u] | 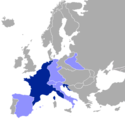 | 1811 | 30,3 w 1811 | 2,9% (30,3 mln na 1050 mln w 1811) | |
| Sułtanat Mameluków | An-Nasir Muhammad | 2,1 |  | 1300 | ||
Abd al-Aziz ibn Saud | 2,0 |  | od 1932[v] | 33 w 2018 | 0,43% (33 mln na 7530 mln w 2018) | |
| Cesarstwo zachodniorzymskie |  Flawiusz Honoriusz | 2,0 | 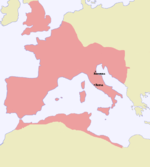 | 395[w] | 22[27] w IV w. | 12,4% (22 mln na 178 mln w 400[13]) |
| Emirat Saffarydów | Amr Ibn Lajs | 2.0 |  | 900 | ||
| Muhammad an-Nasir | 2,0 |  | 1200[6] | |||
| Państwo Inków |  Huayna Capac | 2,0 |  | 1527[6] | ||
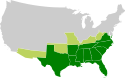
 Jefferson Davis | 2,0 |  | 1861–1865 | 9,1 w 1865 | 0,65% (9,1 mln na 1400 mln w 1865) | |
Jerzy VI | 2 | 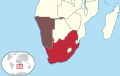 | 1949–1990 (aneksja Namibii) | 35 w 1990 | 0,66% (35 mln na 5300 mln w 1990) | |
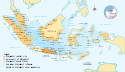
 Sukarno | 1,9 | 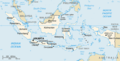 | od 1945[q][x] | 264 | 3,5% (264 mln na 7530 mln) | |
| Chanat Syberyjski | Ibak-Irahim | 1,8 |  | 1520 | ||
 Idris I | 1,78 |  | od 1951[q] | 6,4 w 2018 | 0,08% (6,4 mln na 7530 mln) | |
| Królestwo Indo-Partów | Gondofares | 1.5 |  | 50 | ||
| Królestwo Indo-Scytów | Maues | 1,5 |  | 90 | ||
 Bogda Chan | 1,5 |  | od 1911[y] | 3 w 2018 | 0,04% (3 mln na 7530 mln w 2018) | |
| Imperium Nowoasyryjskie | Aszurbanipal | 1,4 | 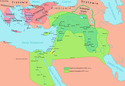 | 697 p.n.e.[6][22] | ||
| Songhaj | Askia Muhammad | 1,4 |  | 1500[28] | ||
 Modibo Keïta | 1,4 | 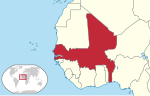 | 1959-1960 | 7,5 w 1960 | 0,25% (7,5 mln na 3000 mln w 1960) | |
| Imperium Harszy | Harsza | 1,35 |  | 625–648[6] | ||
 Haile Selassie I | 1,3 |  | 1952–1993[z] | 48 w 1990 | 0,9% (48 mln na 5300 mln w 1990) | |
| Imperium Mali | Ko Mamadi | 1,29 |  | 1312[29] | 45 w poł XV w. | 10,0% (45,0 mln na 450 mln[30] w poł w. XV) |
François Tombalbaye | 1,28 |  | od 1960[q] | 15 w 2018 | 0,2% (15 mln na 7530 mln w 2018) | |
 Hamani Diori | 1,26 |  | od 1960[q] | 21,5 w 2018 | 0.3% (21,5 mln na 7530 mln w 2018) | |
| Aksum | Ezana | 1,25 |  | 350[6] | ||
 Agostinho Neto | 1,25 |  | od 1975[q] | 17 | 0,2% (na 7000 w 2011) | |
| Imperium Frankijskie |  Karol Wielki | 1,2 | (c) GFDL, CC BY-SA 3.0 | 814[6] | ||
 Gamal Abdel Naser | 1,18 |  | 1959–1961[aa] | 32 | 1,07% (32 mln na 2982 mln w 1961) | |
 Zygmunt III | 1,15[31] |  | 1618[ab]–1621 | 10 | 1,8% (10 mln na 546 mln w 1620[13]) | |
| I Państwo Bułgarskie |  Symeon I | 0,8 |  | 681–1018 | 4 | 1,6% (4 mln na 255 mln w 1000[13]) |
Zobacz też
Uwagi
- ↑ Osoba sprawująca urząd głowy państwa w momencie osiągnięcia przez dane imperium największego terytorium, lub powstania danego państwa w takich rozmiarach.
- ↑ W 1922 Imperium Brytyjskie – metropolia (Wielka Brytania), kolonie, dominia, terytoria mandatowe. Dominia w tym czasie były de facto samorządnymi państwami powiązanymi z Wielką Brytanią unią personalną (wspólny król), po tym jak w 1919 zostały dopuszczone na równi z suwerennymi państwami do grona sygnatariuszy traktatu wersalskiego i członków-założycieli Ligi Narodów. W 1922 Imperium Brytyjskie bez dominiów obejmowało 13,7 mln km² (co dawałoby mu 7. miejsce w rankingu).
- ↑ Michaił Kalinin był symboliczną głową państwa ZSRR jako Przewodniczący Prezydium Rady Najwyższej. Faktycznie przywódcą państwa był Józef Stalin jako sekretarz generalny KC KPR(b), WKP(b) i KPZR, oraz przewodniczący Rady Komisarzy Ludowych a potem Rady Ministrów ZSRR; oraz jako Marszałek (generalissimus) Związku Radzieckiego.
- ↑ Rosja – jako Federacja Rosyjska powstała w 1991 po rozpadzie Związku Radzieckiego.
- ↑ Liczba osób spisanych w 1851 wyniosła 432 164 047 zgodnie z Draft History of Qing.
- ↑ Aneksja Wyspy Hans
- ↑ Chińska Republika Ludowa proklamowana w 1949 roku.
- ↑ od przyłączenia Makau do ChRL
- ↑ Amerykańskie Imperium kolonialne od zdobycia Filipin i Portoryko w wojnie amerykańsko-hiszpańskiej do uzyskania niepodległości przez Filipiny.
- ↑ Wystąpienie Urugwaju.
- ↑ 1939-(retroakcja) wejście w życie Statutu Westminsterskiego stwierdzającego niepodległość Australii. Wówczas państwo administrowało Terytorium Papui i Nowej Gwinei (wcześniej Papua oraz Nowa Gwinea Australijska).
- ↑ 1942: apogeum podbojów Cesarstwa Japonii w czasie II wojny światowej – Japonia + terytoria mandatowe + obszary okupowane (Indochiny, Malaje, część Chin, Holenderskie Indie Wschodnie i niektóre wyspy Pacyfiku.
- ↑ „Rzesza Wielkoniemiecka” łącznie z obszarami okupowanymi nie wcielonymi do III Rzeszy, np. komisariaty na zajętych obszarach Związku Radzieckiego.
- ↑ aneksja Sikkimu
- ↑ W skład duńskiego imperium kolonialnego wchodziły Dania, Norwegia, Islandia i Grenlandia.
- ↑ przyłączenie Patagonii
- ↑ a b c d e f Uzyskanie niepodległości.
- ↑ Objęcie mandatu nad Ruanda-Urundi do uzyskania niepodległości przez Kongo Belgijskie.
- ↑ Do czasu uzyskania niepodległości do powstania Sudanu Południowego.
- ↑ Ostateczne przyłączenie (pokonanie secesji) Katangi.
- ↑ I Cesarstwo Francuskie pod panowaniem Napoleona I łącznie z państwami zależnymi (Księstwo Warszawskie, Związek Reński, Hiszpania i Włochy).
- ↑ Powstanie Królestwa Arabii Saudyjskiej.
- ↑ Podział Cesarstwa Rzymskiego.
- ↑ W latach 1976–2002 częścią Indonezji był de facto Timor Wschodni.
- ↑ Niepodległość od Chin jako Mongolia Zewnętrzna.
- ↑ Łącznie z Erytreą.
- ↑ Zjednoczona Republika Arabska powstała 1 lutego 1958 roku w wyniku połączenia połączenia Egiptu i Syrii. 29 września 1961 w Syria w wyniku zamachu stanu, wycofała się z unii. Egipt zachował nazwę Zjednoczonej Republiki Arabskiej aż do 1971 roku.
- ↑ po rozejmie z Rosją w Dywilinie
Przypisy
- ↑ Ferguson, Niall (2004). Empire, The rise and demise of the British world order and the lessons for global power. Basic Books. ISBN 0-465-02328-2.
- ↑ Harrison Moore: The Dominions of the British Commonwealth in the League of Nations, International Affairs, s. 373, rok 1931.
- ↑ F. R. Scott (January 1944). „The End of Dominion Status”. The American Journal of International Law (American Society of International Law) 38 (1): 34–49.
- ↑ Mark Harrison: The Economics of World War II: Six Great Powers in International Comparison, 1998.
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20120819050341/http://jwsr.ucr.edu/archive/vol12/number2/pdf/jwsr-v12n2-tah.pdf s.222 Jonathan M. Adams, Thomas D. Hall and Peter Turchin (2006). „East-West Orientation of Historical Empires” (PDF). Journal of World-Systems Research (University of Connecticut) 12 (no. 2): 219-229.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac Peter Turchin, Thomas D. Hall and Jonathan M. Adams, „East-West Orientation of Historical Empires”, Journal of World-Systems Research Vol. 12 (no. 2), pp. 219-229 (2006).
- ↑ a b c d Gordon (2005)
- ↑ Inwazja Rosji na Ukrainę (2022)
- ↑ Mały słownik kultury świata arabskiego. Warszawa: Wiedza Powszechna, 1971. Hasło: Omajjadzi w Damaszku, s. 415.
- ↑ a b McEvedy and Jones (1978).
- ↑ Hans - nietypowa walka Kanady i Danii o bezludną wyspę, turystyka.wp.pl.
- ↑ 2011 Census Profile, Statistics Canada [dostęp 2013-03-29] [zarchiwizowane z adresu 2012-02-26] (ang.)., dostępna .
- ↑ a b c d e f Human Population Through Time. American Museum of Natural History 2016-11-04. [dostęp 2018-11-01].
- ↑ Vasseghi, Sheda
- ↑ The other Iran story: Re-engineering the nation's cultural DNA. worldtribune.com. [zarchiwizowane z tego adresu (2016-08-21)].”, Breaking... WorldTribune.com World Tribune News, (12 October 2009).
- ↑ Alfred Cook, Psychology, an Account of the Principal Mental Phenomena 27.
- ↑ International Programs - People and Households - U.S. Census Bureau, census.gov [dostęp 2017-11-25].
- ↑ Steele, Christy, „Rome”, p. 36 (2001).
- ↑ Mclynn Frank „Marcus Aurelius” p. 4. wyd. The Bodley Head 2009
- ↑ Roman Empire Population s. 65.
- ↑ Mclynn Frank „Marcus Aurelius” p. 4. Wyd. The Bodley Head 2009
- ↑ a b c d e Rein Taagepera „Size and Duration of Empires Growth-Decline Curves, 3000 to 600 B.C.”, Social Science Research Vol. 7, 180-196 (1978).
- ↑ Colin McEvedy y Richard Jones (1978), „Atlas of World Population History”, Facts on File (p. 342-351). New York.
- ↑ Thomlinson (1975, Tabla 1).
- ↑ History Chola Empire – History Of Ancient, Medieval And Modern India.
- ↑ Harrison (1998, p. 3,7).
- ↑ Populacja Imperium Rzymskiego « IMPERIUM ROMANUM, „IMPERIUM ROMANUM” [dostęp 2018-11-01] (pol.).
- ↑ John O. Hunwick: Timbuktu and the Songahy Empire: Al-Sa’di’s Ta’rikh Al-sudan Down to 1613 and other Contemporary Documents (Brill, 2003), p. xlix.
- ↑ Hempstone, s. 312
- ↑ Walker, Sheila S., African roots/American cultures: Africa in the creation of the Americas, Publicado por Rowman & Littlefield, p. 127. (2001)
- ↑ Mariusz Trąba, Lech Bielski: Władcy i królowie Polski. Warszawa: Reader’s Digest, 2005, s. 444. ISBN 83-60123-13-6.
Media użyte na tej stronie
Flaga Rosji 1858—1883
Alexandre Millerand
Flag of Canada introduced in 1965, using Pantone colors. This design replaced the Canadian Red Ensign design.
The flag of Navassa Island is simply the United States flag. It does not have a "local" flag or "unofficial" flag; it is an uninhabited island. The version with a profile view was based on Flags of the World and as a fictional design has no status warranting a place on any Wiki. It was made up by a random person with no connection to the island, it has never flown on the island, and it has never received any sort of recognition or validation by any authority. The person quoted on that page has no authority to bestow a flag, "unofficial" or otherwise, on the island.
Autor: F l a n k e r, Licencja: CC BY-SA 2.5
Łatwo można dodać ramkę naokoło tej grafiki
Bundesflagge und Handelsflagge des Norddeutschen Bundes (1866-1871) und Reichsflagge des Deutschen Reiches (1871-1918)
Bundesflagge und Handelsflagge des Norddeutschen Bundes (1866-1871) und Reichsflagge des Deutschen Reiches (1871-1918)
The Flag of India. The colours are saffron, white and green. The navy blue wheel in the center of the flag has a diameter approximately the width of the white band and is called Ashoka's Dharma Chakra, with 24 spokes (after Ashoka, the Great). Each spoke depicts one hour of the day, portraying the prevalence of righteousness all 24 hours of it.
The national flag of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Created according to the 2006 constitution : Son emblème est le drapeau bleu ciel, orné d’une étoile jaune dans le coin supérieur gauche et traversé en biais d’une bande rouge finement encadrée de jaune. (Its symbol is a sky blue flag, decorated with a yellow star in the upper left corner and crossed in the diagonal by a red strip with thin yellow borders) It seems to be identical, except for a lighter field hue, to the 1966–1971 flag.
Jefferson Davis
Flag of South Africa, also known as the Oranje-Blanje-Blou, used from 31 maja 1928 until 27 kwietnia 1994
bendera Indonesia
The flag of the Ethiopian Empire with the Lion of Judah in the center
Please do not replace the simplified code by a version created with Inkscape or another vector graphics editor❗
Łatwo można dodać ramkę naokoło tej grafiki
Autor:
- Angola_1978.jpg: Chaplin2222
- derivative work: Makakaaaa (talk)
Ambasador Polski w Angoli, gen. dyw. Roman Paszkowski z małżonką Aleksandrą (z prawej) składają życzenia noworoczne Prezydentowi Ludowej Republiki Angoli, Agostinho Neto i jego małżonce Eugenii z okazji Nowego Roku 1978, Luanda, Angola.
Flaga Rosji 1858—1883
Hirohito in dress uniform
Autor: Кардам, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Miniatura del zar Simeón el Grande en el Madrid Skylitzes
Autor: Autor nie został podany w rozpoznawalny automatycznie sposób. Założono, że to Huhsunqu (w oparciu o szablon praw autorskich)., Licencja: CC BY-SA 2.5
Flag of Peru-Bolivian Confederation.
Autor: Gabagool, Licencja: CC BY 3.0
Locator map of the Gökturks, c. 551-572. (Partially based on Atlas of World History (2007) - The World 500-750, map)
The flag of the Ethiopian Empire with the Lion of Judah in the center
Autor: Vaskots7 & NuclearVacuum, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Първо Българско Царство
Mapa Demokratycznej Republiki Konga z CIA
Autor: Classical Numismatic Group;[1], Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Coin of the Baktrian king Demetrios II
(c) GFDL, CC BY-SA 3.0
Mapa rozwoju Imperium Franków w latach 481-814
Autor: Original: Astrokey44 Vectorizaton: Chabacano, Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Ta ^specifik^ z W3C grafika wektorowa została stworzona za pomocą Inkscape .
Autor: Original: Astrokey44 Vectorizaton: Chabacano, Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Mapa del es:Imperio de Mali
Autor: Pryaltonian, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Map of the Qing Dynasty in 1820, representing its stablized territory from 1790-1839. (Includes provincial boundaries and the boundaries of modern China for reference.) Provinces in yellow, military governorates and protectorates in light yellow, tributary states in orange.
Adapted from File:ROC_PRC_comparison_eng.jpg and information complied from:
- http://baike.baidu.com/view/5405.htm
- http://map.huhai.net/58-59.jpg
- http://www.sina7.com/jdwh/UploadFiles_6109/200709/20070918093610860.jpg
- File:China_and_Japan,_John_Nicaragua_Dower_(1844).jpg
- File:Carte_generale_de_l'Empire_Chinois_et_du_Japon_(1836).jpg
- File:Empire_Chinois,_Japon_(1832).jpg
- File:L'Empire_Chinois_et_du_Japon_(1833).jpg
- http://city.udn.com/3011/4192243?tpno=48&cate_no=0
- http://bbs.godeyes.cn/showtopic-371673.aspx
Ilkhanate in 1256–1353
Autor:
- File:First Brazilian Empire (orthographic projection).svg: Heraldry
- derivative work: Jon C (talk)
Empire of Brazil at its largest territorial extent, 1822–1828, including former Cisplatina province.
Mapka Kazahstanu z CIA Factbook
Autor: Ningyou., Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Flag with the cross of Burgundy (saltire). Also named Cross of Burgundy flag. It was used in the Catholic Monarchy and in its viceroyalties such as New Spain and Peru. It was also used by Spain as a military or king flag. Used by the Carlist movement.
Autor: Ro4444, Licencja: CC BY-SA 4.0
Approximate extent of the Khanate of Sibir in the fifteenth-sixteenth centuries. Revised version of File:Siberian Khanate map English.svg. Based on the map "Russian state in the XVI - early XVII centuries (1490-1618)" in World History, Volume IV, Moscow: Soviet Academy of Sciences, 1958.
Flag of the Chinese Empire under the Qing dynasty (1889-1912), details per the restoration of Beiyang fleet researcher [1].
Autor: Gabagool, Licencja: CC BY 3.0
Locator map of the Kara Khitais, c. 1200. (Partially based on Atlas of World History (2007) - The World 1000-1200, map)
The extent of the Eastern (Byzantine) and Western Roman Empires in 550.
Autor: unknown, Licencja: CC BY-SA 2.5
Ja, właściciel praw autorskich do tego dzieła, udostępniam je na poniższej licencji
Autor: Gabagool, Licencja: CC BY 3.0
Locator map of the Mughal Empire, c. 1700. (Partially based on Atlas of World History (2007) - The World 1600-1700, map)
Age of the Caliphs
The Ottoman Empire during the 17th century
Autor: The White House, Licencja: CC BY-SA 4.0
This official White House photograph is being made available only for publication by news organizations and/or for personal use printing by the subject(s) of the photograph. The photograph may not be manipulated in any way and may not be used in commercial or political materials, advertisements, emails, products, promotions that in any way suggests approval or endorsement of the President, the First Family, or the White House.
Flag of South Africa, also known as the Oranje-Blanje-Blou, used from 31 maja 1928 until 27 kwietnia 1994
Map of Niger.
Original caption:
- François Tombalbaye marching in a parade celebrating the tenth anniversary of independence (1970).
Autor: Autor nie został podany w rozpoznawalny automatycznie sposób. Założono, że to World Imaging (w oparciu o szablon praw autorskich)., Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Map of the Greco-Bactrian at its maximum extent, circa 180 BC. Personal creation.
A map of the British Empire in 1921 when it was at its height, just before the Anglo-Irish Treaty of 1921.
(But 1921-1937 Ireland continued to have the same status as Canada, Newfoundland, the South African Union, Australia and New Zealand, that is to be part of the British Empire as a dominion)
Head of Trajan (reign 98–117 CE), from an oversized statue (around 2.70 m height).
Mapa Asyrii w 824 i 671 r. p.n.e.
Harsha Empire
Ahmed Ben Bella (أحمد بن بلّة) (born December 25, 1918)
Extensión del Imperio romano de occidente en 395.dC, a la muerte de Teodosio I.
Autor:
- MacedonEmpire.jpg: Captain Blood (talk)
- Mapa_de_Alejandrías.svg: *Alexander_III_empire_map-es.svg: *Alexander_III_empire_blank_map.svg: historicair 22:06, 18 August 2007 (UTC)
- Alexander_III_empire_map-fr.svg: historicair 23:11, 18 August 2007 (UTC)
- derivative work: Mircalla22 (talk)
- derivative work: Mircalla22 (talk)
- derivative work: Mircalla22 (talk)
Map of Macedonian Empire under Alexander III "The Great" command in Antic period
A map depicting the extent the Safavid Empire at its greatest extent under Ismail I.
Imperio Portugués
Green: Anglo-Egyptian Sudan
Light green: Ceded to Italian Libya in 1919[1]
Dark gray: Egypt and the United Kingdom
Autor: Red4tribe, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
The Dutch Empire during the 17th and 18th centuries: in light green the Dutch East India Company, in dark green is the Dutch West India Company. In yellow the territories occupied later, during the 19th century.
Map of the en:Kara-Khanide khanates copied from de:Karachaniden to fr:Qarakhanides
El mariscal Andrés de Santa Cruz
Autor: Gabagool, Licencja: CC BY 3.0
Locator map of Khazaria, c. 750. (Partially based on Atlas of World History (2007) - The World 500-750, map)
'Portrait of the Qianlong Emperor in Court Dress
Autor: Gabagool, Licencja: CC BY 3.0
Ayyubid dynasty at its greatest extent, founded by Saladin c. 1188.
(c) Venu62, CC-BY-SA-3.0
Opis
This Map was created using the Blank World Map available at Wiki:Maps.Autor: Gabagool, Licencja: CC BY 3.0
Locator map of the Kievan Rus, c. 1000. (Partially based on Atlas of World History (2007) - The World 750-1000, map)
The German emperor, king Wilhelm II v. Prussia (in 1859-1941, reign 1888-1918), in Prussian officer's uniform (Überrock). The simple Überrock with small order decoration was the knock about clothes of the military. Orders: Cervical orders: Protector cross of the Maltese Knight's order. In the buttonhole: the military order of savoy
Sukarno, pierwszy prezydent Indonezji
Autor: TUBS
Location of XY (see filename) in the region.
King Idris I of Libya
Autor: Autor nie został podany w rozpoznawalny automatycznie sposób. Założono, że to World Imaging (w oparciu o szablon praw autorskich)., Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Coin of Antimachus. Cabinet des Medailles, Paris. Personal photograph 2006.
Autor:
Portrait of Alexander the Great. Marble, Hellenistic artwork, 2nd-1st century BC. Said to be from Alexandria, Egypt.
Painting, portrait of Nadir Shah seated on a carpet, oil on canvas, probably Tehran, 1780s or 1790s
This painting is a portrait of Nadir Shah Afshar, one of the most important figures in Iranian history of the last 300 years. Nadir Shah was a brilliant military commander of humble origins who rose through the ranks due to his talent. He was a key figure in the restoration of order in Iran after the Afghan invasion of his country in 1722. At first, he worked in the name of members of the previous dynasty, the Safavids. In 1736, however, he declared himself Shah, and he ruled with considerable success until his assassination in 1747. He established a large and effective army that had few rivals in Asia. With it he repulsed the Ottomans and Russians from Iranian territory and conducted a successful invasion of the Mughal empire in what is now Pakistan and northern India. He defeated the Mughal army in 1739 and seized the capital, Delhi. Among the loot he acquired was the Mughal emperor's jewels, which are still kept in the Central Bank of Iran in Tehran.
This is one of only two portraits of Nadir Shah in oils that survive, but they both seem to date from the late 18th century, several decades after his death. The Shah is shown wearing weapons and other accoutrements (armbands, belt, hat band etc.) that are jewelled with precious stones understood to be from the Mughal treasure. The carpet on which he sits is also Mughal.
Painting, oil pigments on canvas, portrait of Nadir Shah.
Frame height: 179cm
Frame width: 116.5cm
Weight: 60kg (Rough estimate of weight framed and glazed)
Frame depth: 7.5cmAutor: Milenioscuro, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Flag of the Gran Colombia, used between October 6, 1821 and December 17, 1831.
Autor: Gabagool, Licencja: CC BY 3.0
Locator map of the Almohad dynasty at its greatest extent, c. 1200. (Partially based on Atlas of World History (2007) - The World 1000-1200, map)
Portrait of former president of Argentina, General Julio Argentino Roca.
Indonesia map from the CIA World Factbook website
Coin of the Axumite king Ezana
Coin of Vonones I of Parthia from the mint at Ecbatana. The Greek inscription on the obverse reads ΒΑϹΙΛΕΥϹ (king). The reverse shows Nike with a palm. The inscription reads ΒΑϹΙΛΕΥϹ ΟΝΩΝΗϹ ΝΕΙΚΗϹΑϹ ΑΡΤΑΒΑΝ[ΟΝ]. From [1]
Autor: Milenioscuro, Licencja: CC BY-SA 4.0
Locator map of Mali Federation (january-march 1959)
Autor: Ta ^specifik^ z W3C grafika wektorowa została stworzona za pomocą Inkscape ., Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
The Russian Empire in 1867.
Autor: Kasper Holl, Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Denmark-Norway and possessions in 1800. Other international borders represent the situation in the 1710s.
Flag of the First Empire of Brazil, with 19 stars representing the provincies by the time.
Flag of Mexico (1821-1823)
Autor: self, based on WP locator maps Category:Locator maps, Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Seleucid Empire ca. 323 BCE (at the time of Alexander's death)
Autor: Autor nie został podany w rozpoznawalny automatycznie sposób. Założono, że to World Imaging (w oparciu o szablon praw autorskich)., Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Gold coin of w:Khosrau II. Cabinet des Medailles. Personal photograph 2007.
© Giggette / Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 3.0
Political divisions of 1821 Mexico.
Mapa Libii na podstawie CIA World Factbook
Autor: Officia do Palácio do Planalto, Licencja: CC BY 2.0
General Secretary of the Communist Party of China, Xi Jinping during an audience held at the Brazilian Palácio do Planalto with Vice President of Brazil Hamilton Mourão
М. И. Калинин, Москва
First French Empire in 1812.
Indo-Greek map in color. Personal drawing 2007.
Autor: Milenioscuro, Licencja: CC BY-SA 4.0
Locator map of Union of South Africa (1915-1961)
(c) Classical Numismatic Group, Inc. http://www.cngcoins.com, CC-BY-SA-3.0
Toramana portrait from coin
Autor: Gabagool, Licencja: CC BY 3.0
Locator map of the Chagatai Khanate, c. 1300. (Partially based on Atlas of World History (2007) - The World 1200-1300, map)
Autor: Milenioscuro, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Peru–Bolivian Confederation (orthographic projection)
Charlemagne, by Albrecht Dürer, the anachronistic coat-of-arms above him show the German eagle and the French Fleur-de-lis.
Ottoman flag after the mid-19th century (before that time, the star was usually 8-pointed, not 5-pointed).
Map of Kushan Kingdom (ukrainian)
Autor: User:Stannered, Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Attributed flag of the Timurid Empire (the reference dates to 1374-5, but it it not necessarily the design of any flag in actual use).
(Quote from original by en:User:Ingoman) Flag of the Timurid Empire according to the Catalan Atlases c.1374-5 created by James Dahl The three bezants arranged in a triangle is the "Symbol of Peace". I have seen a variant shown of this flag which has the bezants pointing upwards, and they are white on a light blue background, but I have found no evidence to support this, and it is doubtless a reconstruction based on coinage (which also features the Symbol of Peace) with the colours a matter of congecture. However, in historical accounts of the flag of Tamerlane, he is always described as bearing a flag of black, red and white, which Europeans incorrectly interpret as a tricolour for lack of a description of the flag's devices. (the white is probably a fringe). Since I have never found reason to doubt the accuracy of the Catalan Atlas in terms of flags (it has proven in fact to be the most trustworthy document of the time period) I have concluded that this in fact was Timur's flag.(c) Bundesarchiv, Bild 183-S33882 / Nieznany / CC-BY-SA 3.0
Adolf Hitler, faschistischer Führer, Hauptkriegsverbrecher. geb. 20.4.1889 in Braunau (Inn), gest. (Selbstmord) 30.4.1945 in Berlin übernahm als Reichswehrspitzel 1921 die Führung der NSDAP; stand im November 1923 an der Spitze eines konterrevolutionären Putschversuchs in München (Hitler Putsch). Am 30.1.1933 wurde Hitler Reichskanzler; damit begann die Errichtung der Diktatur des reaktionärsten und aggresivsten Teils der deutschen Finanzbourgeoisie. Am 2.8.1934 wurde er Nachfolger Hindenburgs als Staatsoberhaupt; 1938 Oberbefehlshaber der Wehrmacht. Als Werkzeug des deutschen Imperialismus konzipierte Hitler Wege und Methoden, um dessen Aggressionsziele und Weltherrschaftsziele durchzusetzen. UBz: Porträtaufnahme vom 20.4.1937. 2754-49
[Adolf Hitler (Porträt)]
Abgebildete Personen:
- Hitler, Adolf: Reichskanzler, Deutschland
Autor: Exa, Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Kolonie niemiecckie
medal coin of 1000FF, with portrait of the first president of Niger, Hamani Diori
Autor: Autor nie został podany w rozpoznawalny automatycznie sposób. Założono, że to World Imaging (w oparciu o szablon praw autorskich)., Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Map of the expansion of the Indo-Scythians in India. Personal creation.
Shaded relief map of Ethiopia, 1999, produced by the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency.
Malik-Shah I
Autor: Ssolbergj, Licencja: CC BY-SA 4.0
The People's Republic of China (green) and its claimed territory (lighter green).
Autor: Milenioscuro, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Japanese Empire.
Autor: Vorziblix, Licencja: CC0
The flag of the Golden Horde, as shown in Angelino Dulcert's 1339 map. A similar flag appears in the later Catalan Atlas (1375), providing corroboration.
See also Early Mongol Flags at crwflags.com:
- One of the charges is a crescent and the other looks like a simplified form of the tamga from the flag of Idel Ural. On different copies of the flag, the crescent has different size; it is often smaller than shown here, sometimes even reduced into a simple oblique stroke and conjoined with the other charge into a si[n]gle symmetrical object; the other charge also sometimes lacks the oblique part [2, 3]. It was obviously difficult to draw the charges always the same way. The cities with this flag which are easy to identify are [2, 7, 8]: Sarai, the capital (spelled Sarra) - there is also a depiction of the ruler, "Jani Beg Lord of Sarai" ("Jambech senyor de Sarra"); Tana, present-day Azov, Russia; and Urgench, Uzbekistan (spelled Organci, with a cedilla under the c; nowadays ruined). This flag is a variant of the flag of "Emperor of Sarai" ("Emperador de Sara") from "Libro del conoscimiento de los reinos" [7] and might be the one that had really existed, considering the similarity of its charges with those from the flag of Idel Ural.
- [2] Enciclopedia universal ilustrada, vol. XXI, Espan~a Madrid: Espasa-Calpe S.A., 1968
- [3] Istorija otkric'a i istraz<ivanja, vol. I: Poc<etak istraz<ivanja; Mladinska knjiga, Ljubljana, 1979; Original title: A History of Discovery and Exploration, vol. I: The Search Begins;(C) 1973 Aldus Books Limited, London
- [7] Libro del Conoscimiento. Viajes medievales, vol. I Madrid: Fundacio'n Jose' Antonio de Castro, 2005 ISBN 84-96452-11-5 (complete edition) ISBN 84-96452-12-3 (vol. I) [e9s50]
- [8] A[p]pendices. (Ibid.)
- Tomislav Todorovic, 21 April 2007
Autor: Thomas Lessman (Contact!), Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Eastern Hemisphere in 800 AD.
波斯史书《成吉思书》(Chingiznama)中记载征伐窝阔台汗国察八儿汗,金帐大汗脱脱汗在泽拉夫尚河畔会见察合台汗国怯别汗的画像
Autor: Autor nie został podany w rozpoznawalny automatycznie sposób. Założono, że to World Imaging (w oparciu o szablon praw autorskich)., Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Map of the Indo-Parthian Kingdom — in the 130s CE.
Autor: NuclearVacuum, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Location of the United Arab Republic
A half-length portrait of Mexican Emperor Agustín I attributed to Josephus Arias Huerta.
Autor: Jungpionier, Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Ausdehnung und Gebietserweiterung des Delhi-Sultanats zu Beginn der Tughluq-Dynastie (ca. 1320-1330)
Autor: Gabagool, Licencja: CC BY 3.0
Map of the Abbasid Caliphate at its greatest extent, c. 850. (Partially based on Atlas of World History (2007) - Progress of Islam, map)
Autor: Ssolbergj (talk), Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
India. Area controlled by India in dark green; claimed but not controlled areas in light green.
Autor: Olek Remesz (wiki-pl: Orem, commons: Orem), Licencja: CC BY-SA 2.5
Chorągiew królewska z okresu panowanie dysastii Wazów (1587-1668) w Polsce
Autor: Morgan Hauser, derived from File:Second world war europe 1943-1945 map en.png and File:Second world war europe 1941-1942 map en.png by users Jarry1250 and ArmadniGeneral, respectively., Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Europe at the height of the WWII Axis military conquests in 1941–1942.
Autor: Anonymus 88, Licencja: CC0
Map of all possessions of Bourbon Spain during the period 1700-1810
Autor: Ssolbergj, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (Soviet Union)
Autor: MapMaster, Licencja: CC BY-SA 4.0
A map showing the Great Seljuk Empire at its height, upon the death of Malik Shah I in 1092.
- The capital of the Great Seljuk Empire is shown at Ishfahan (Persia/Iran).
The borders of present-day countries are shown in gray.
The lighter colour in the top right represents Karakhanids.
- "In 1089, Malik Shah returned to the charge, occupied Bukhara, captured Sarakand, and imprisoned the Karakhanid Ahmed . . . whom he later reinstated as client-ruler. From that time forward, the Karakhanids who reigned in Bukhara and Samarkand did so as lieutenants of the Seljuk sultans. Transoxiana was now no more than a dependency of the Seljuk Empire."
(Grousset p. 147.) - Other areas such as the Danishmends are not shown separately.
- The locations of the Battle of Manzikert (1071) and the Battle of Dandanaqan (1040) are also shown.
Autor: India Post, Government of India, Licencja: GODL-India
Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed
Autor:
- Blank US Map.svg: Theshibboleth
- derivative work: Nkocharh
A map of the Confederate States of America, Maryland and claimed states and territories.
Legend:
Autor: , Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Map showing the extent of the Rashtrakuta, Rajput and Pala empires.
Retrato del príncipe de Asturias Carlos de Borbón (1748-1819), que fue hijo del rey Carlos III de España y llegaría a reinar en España como Carlos IV.
(c) Arab League z angielskiej Wikipedii, CC-BY-SA-3.0
Khwarezmian Empire (1190-1220)
The principal forts, trading posts and colonies of the Portuguese Empire (1415-1999).
Abbreviations:
disc: date of discovery est: date of establishment ind: date of independence
Present-day Portuguese territory is underlined in green.Flag of the Almohad dynasty (1130-1269)
Autor: user:shakko, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Timur. Forensic facial reconstruction by M.Gerasimov. 1941
Portrait of Shah Ismail I of Persia (1487-1524)
Autor: UnixBased, Licencja: CC BY-SA 4.0
Russia on the globe with the annexed territories marked as claimed
Autor: Tintazul, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Map of the Persian Afsharid Dynasty (1736–1802)
Autor: Gabagool, Licencja: CC BY 3.0
Locator map of the Fatimid Caliphate, c. 969. (Partially based on map: [1])
Autor:
- Unia_polsko-litewska_w_1635.png: *Polish-Lithuanian_Commonwealth_1635.png: user:Mathiasrex, Maciej Szczepańczyk; based on layers of user:Halibutt
- derivative work: Alokasta (talk)
- derivative work: Hoodinski
Rzeczpospolita Obojga Narodów 1635 r.
Khan Oljaitu accepts Yuan ambassadors, as featured in Compendium of Chronicles of Rashiduldin Hamadani, kept at British Museum in London
Autor: F l a n k e r, Licencja: CC BY-SA 2.5
Łatwo można dodać ramkę naokoło tej grafiki
Portrait of Napoleon in Coronation Robes (detal)
Łatwo można dodać ramkę naokoło tej grafiki
William McKinley, Präsident der Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika
Autor: Gabagool, Licencja: CC BY 3.0
Locator map of Tibet at its peak, c. AD 800. (Partially based on Atlas of World History (2007) - The World 750-1000, map)
(c) Government.ru, CC BY 4.0
Prime Minister Mikhail Mishustin with President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev in Astana.
Autor: Angelus, Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Map of the Roman Empire at its height, under Trajan.
Autor: Gabagool, Licencja: CC BY 3.0
Locator map of the Hephthalite Khanate of the White Huns, c. 500 in Central Asia. (Partially based on Atlas of World History (2007) - The World 250-500, map)
Autor: Gabagool, Licencja: CC BY 3.0
Map of the Mamluk sultanate of Egypt, AD 1279. (Partially based on [1])
The Ayyubid dynasty is often represented by the colour yellow.
"The Ayyubids and Mamluks, who succeeded the Fatimids in Egypt and Syria, retained the association of yellow with the ruler. Salah al-Din (Saladin), the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty, carried a yellow flag emblazoned with an eagle, supposedly inherited from the Zangid dynasty, whose protégé he had been." Jane Hathaway, A Tale of Two Factions: Myth, Memory, and Identity in Ottoman Egypt and Yemen, p. 97.Autor: Gabagool, Licencja: CC BY 3.0
Locator map of the Golden Horde, c. 1300. (Partially based on Atlas of World History (2007) - The World 1200-1300, map)
Flag which can be used to represent the Abbasid Caliphate. Note that the concept of rectangular national flags did not exist during Abbasid times, but black was the dynastic color of the Abbasids (just as green was the dynastic color of the Fatimids, etc.), and the "black banner" of the Abbasids is famous in Islamic history.
Autor: Gunawan Kartapranata, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
The Nusantara Archipelago during the height of Majapahit Empire in XIV century. The red dot is Trowulan; Majapahit capital city. The dark orange area is core realm of Majapahit on eastern part of Java. The light orange area is vassal states of Majapahit mentioned in Nagarakretagama. The pale yellow is outer realm or independent states from Majapahit. The dark cyan is the sea area under influence or effective control of Majapahit. The light cyan is the extent of Majapahit naval expedition.