Mare Nectaris
| ||
 | ||
| Ciało niebieskie | Księżyc | |
| Średnica krateru | 333 km | |
| Źródło nazwy | "Morze Nektaru" | |
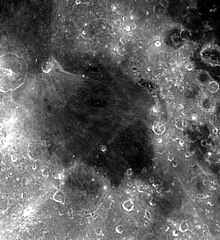
Mare Nectaris (łac. Morze Nektaru) to niewielkie morze księżycowe (obszar pokryty skałami bazaltowymi pochodzenia wulkanicznego, wyraźnie ciemniejszy od pozostałej powierzchni Księżyca) umiejscowione pomiędzy Mare Tranquillitatis (Morzem Spokoju) i Mare Fecunditatis (Morzem Obfitości). Zachodnią granicę Morza Nektaru wyznacza pasmo górskie Pirenejów, po tej samej stronie morza znajduje się też grupa rowów tektonicznych. Jego średnica równa jest 333 km.
Media użyte na tej stronie
Autor:
- Nuvola_apps_kmoon.png: David Vignoni / derivative work: Lady Whistler (talk)
Icon from Nuvola icon theme for KDE 3.x.
cylindrical map projection of the Moon. The Moon's whole surface was mapped by the Clementine spacecraft in 1994, here North is at the top. The dark floor of crater Plato is at the middle top above Mare Imbrium, while the bright floor and rays of crater Tycho is near the middle bottom below Mare Imbrium. Mare Procellarum is at the near left, and Mare Tranquillitatis is just right of centre and Mare Crisium is at the near right. The far left and far right show the contrast of the mostly cratered farside with small isolated mare.
(c) Luc Viatour, CC-BY-SA-3.0
Nearly Full Moon view from earth In Belgium (Hamois).
en:Mare Nectaris is located within the Nectaris basin on the
lunar nearside. The basin material is of the Nectarian, and Lower Imbrian epochs, with the mare material of the Upper Imbrian epoch. The crater Theophilus, on the northeastern side of the mare is of the Eratosthenian epoch. Thus, the crater is younger than the mare to its southeast. Montes Pyrenaeus borders the mare to the west. The crater Fracastorius can be seen at the bottom of the photo. The mare material is approximately 1000 m in depth. Enough subsistence has occured to open a few arcuates grabbens on the western margin of the mare.The crater
in the lower center of the mare is RosseShiny LightSteelBlue button/marker widget. Used to mark the location of something such as a tourist attraction.






