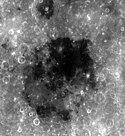
Mare Smythii
| ||
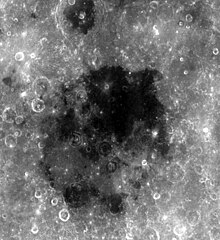 | ||
| Ciało niebieskie | Księżyc | |
| Średnica krateru | 740 km | |
| Głębokość krateru | 5 km | |
| Źródło nazwy | William Henry Smyth | |

Mare Smythii (łac. Morze Smytha) to morze księżycowe położone po widocznej stronie Księżyca. Jego średnica równa jest 373 km. Nazwa pochodzi od nazwiska dziewiętnastowiecznego astronoma brytyjskiego Williama Henry'ego Smytha. Na północ od morza położony jest krater uderzeniowy Neper, zaś na północny zachód od niego kratery Schubert oraz Schubert B. Na południowym brzegu Mare Smythii znajduje się krater Kästner.
Media użyte na tej stronie
Autor:
- Nuvola_apps_kmoon.png: David Vignoni / derivative work: Lady Whistler (talk)
Icon from Nuvola icon theme for KDE 3.x.
Autor: Martin Pauer (Power), Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Vergleich der Topographie der Oberfläche (oben) und des Gravitationsfeldes.
cylindrical map projection of the Moon. The Moon's whole surface was mapped by the Clementine spacecraft in 1994, here North is at the top. The dark floor of crater Plato is at the middle top above Mare Imbrium, while the bright floor and rays of crater Tycho is near the middle bottom below Mare Imbrium. Mare Procellarum is at the near left, and Mare Tranquillitatis is just right of centre and Mare Crisium is at the near right. The far left and far right show the contrast of the mostly cratered farside with small isolated mare.
(c) Luc Viatour, CC-BY-SA-3.0
Nearly Full Moon view from earth In Belgium (Hamois).
en:Mare Smythii is located along the equator on the easternmost edge of the near side. The Smythii basin where the mare is located is of the Pre-Nectarian epoch, while the surrounding features are of the Nectarian system. The mare material, which make up the floor of the mare, is a high alumious basalt, and consists of Upper Imbrian basalt covered by Eratosthenian basalt. The Crater located to the north of the mare, at the top of the photo, is Neper. This crater makes up part of the southern rim of Mare Marginis. Just off to the northwest of the mare are the craters Schubert (top) and Schubert B (bottom). The dark mare filled crater at the southern edge of Smythii is the crater Kastner.
Shiny LightSteelBlue button/marker widget. Used to mark the location of something such as a tourist attraction.