Most (mózg)
Most (most Varola, łac. pons, pons Varoli) – część ośrodkowego układu nerwowego należąca do pnia mózgu.
Stosunki anatomiczne
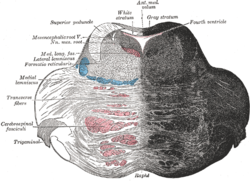
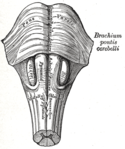
Most posiada dwie części: brzuszną i grzbietową, pokryty jest od zewnątrz oponami mózgowo-rdzeniowymi, które odgraniczają go od kości czaszki. Leży powyżej rdzenia przedłużonego, pomiędzy rdzeniem przedłużonym a śródmózgowiem. Tworzy poprzeczne, szerokie uwypuklenie, widoczne dobrze na brzusznej powierzchni mózgowia. Most jest u góry odgraniczony od konarów mózgu (crura cerebri) przez bruzdę boczną śródmózgowia, a na dole oddziela go od rdzenia przedłużonego wyraźna bruzda opuszkowo-mostowa. W płaszczyźnie pośrodkowej na brzusznej powierzchni mostu biegnie w bruździe podstawnej (sulcus basilaris) tętnica podstawna mózgu (arteria basilaris cerebri), od której odchodzą tętnice zaopatrujące most. W wyniosłościach obok bruzdy tętnicy podstawnej leżą drogi piramidowe. Bocznym przedłużeniem mostu są konary środkowe móżdżku (pedunculi cerebellares medii) stanowiące połączenie z móżdżkiem. Do mostu wnikają również konary górne móżdżku (pedunculi cerebellares superiores) biegnące do śródmózgowia. Część grzbietowa mostu stanowi część dna dołu równoległobocznego (fossa rhomboidea), będącego dnem komory czwartej.
Wewnątrz mostu znajdują się:
- jądra mostu (nuclei pontis),
- twór siatkowaty (formatio reticularis),
- niektóre z jąder nerwów czaszkowych:
- jądro nerwu twarzowego (nucleus nervi facialis),
- jądro nerwu odwodzącego (nucleus nervi abducentis),
- jądra nerwu trójdzielnego (nucleus motorius nervi trigemini, nucleus sensoroius principalis nervi trigemini, nucleus tracti mesencephalici nervi trigemini).
Bibliografia
- Adam Krechowiecki, Florian Czerwiński: Zarys anatomii człowieka. Szczecin: Wydawnictwo Lekarskie PZWL, 2004. ISBN 83-200-3362-4.
- Janina Sokołowska-Pituchowa (red.) Anatomia człowieka. Podręcznik dla studentów medycyny. Wyd. VII. PZWL 2005 ISBN 83-200-3185-0.
| ||||||||||||||||||
![]() Przeczytaj ostrzeżenie dotyczące informacji medycznych i pokrewnych zamieszczonych w Wikipedii.
Przeczytaj ostrzeżenie dotyczące informacji medycznych i pokrewnych zamieszczonych w Wikipedii.
Media użyte na tej stronie
Star of life, blue version. Represents the Rod of Asclepius, with a snake around it, on a 6-branch star shaped as the cross of 3 thick 3:1 rectangles.
Design:
The logo is basically unicolor, most often a slate or medium blue, but this design uses a slightly lighter shade of blue for the outer outline of the cross, and the outlines of the rod and of the snake. The background is transparent (but the star includes a small inner plain white outline). This makes this image usable and visible on any background, including blue. The light shade of color for the outlines makes the form more visible at smaller resolutions, so that the image can easily be used as an icon.
This SVG file was manually created to specify alignments, to use only integers at the core 192x192 size, to get smooth curves on connection points (without any angle), to make a perfect logo centered in a exact square, to use a more precise geometry for the star and to use slate blue color with slightly lighter outlines on the cross, the rod and snake.
Finally, the SVG file is clean and contains no unnecessary XML elements or attributes, CSS styles or transforms that are usually added silently by common SVG editors (like Sodipodi or Inkscape) and that just pollute the final document, so it just needs the core SVG elements for the rendering. This is why its file size is so small.The Star of Life, medical symbol used on some ambulances.
Star of Life was designed/created by a National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (US Gov) employee and is thus in the public domain.Medulla oblongata and pons. Anterior surface.