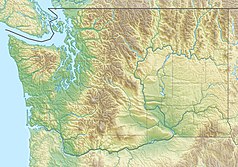
Mount Rainier
 Mount Rainier: widok ze szlaku prowadzącego granią Sourdough. | |
| Państwo | |
|---|---|
| Stan | |
| Położenie | |
| Pasmo | |
| Wysokość | 4392 m n.p.m. |
| Wybitność | 4026 m |
| Pierwsze wejście | Hazard Stevens i P.B. Van Trump |
Mount Rainier lub Mount Tahoma (Tacoma) – stratowulkan w USA, położony 87 km na południowy wschód od Seattle, w stanie Waszyngton. Jest to najwyższy szczyt Gór Kaskadowych, a także najwyższy punkt w stanie Waszyngton. Leży w hrabstwie Pierce, na terenie parku narodowego Mount Rainier. Nazwa pochodzi od nazwiska brytyjskiego admirała Petera Rainiera. Uhonorował go w ten sposób kapitan George Vancouver, który badając pacyficzne wybrzeża Ameryki Północnej 8 maja 1792 roku odkrył szczyt dla Europejczyków[1].
Pierwszego wejścia na szczyt dokonali Hazard Stevens i P.B. Van Trump w 1870 r.
Ostatnia erupcja miała miejsce w listopadzie i grudniu 1894 r., natomiast ostatnia aktywność sejsmiczna w 1969 r.[2]
Mount Rainier był także główną inspiracją dla nazwy szóstego albumu studyjnego Alice in Chains Rainier Fog oraz tytułowego utworu z 2018[3]
Przypisy
- ↑ Cascade Range Volcanoes Volcano Names. U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey. [dostęp 2014-01-09]. (ang.).
- ↑ Rainier. Global Volcanism Program, Smithsonian Institution. [dostęp 2016-02-17]. (ang.).
- ↑ Steve Appleford. Alice in Chains Talk Honoring Seattle Comrades With New Album ‘Rainier Fog’. „Rolling Stone”. ISSN 0035-791X. [dostęp 2018-08-01]. [zarchiwizowane z adresu 2018-06-29]. (ang.).
Linki zewnętrzne
Media użyte na tej stronie
Autor: Uwe Dedering, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Relief location map of the USA (without Hawaii and Alaska).
EquiDistantConicProjection : Central parallel :
* N: 37.0° N
Central meridian :
* E: 96.0° W
Standard parallels:
* 1: 32.0° N * 2: 42.0° N
Made with Natural Earth. Free vector and raster map data @ naturalearthdata.com.
Formulas for x and y:
x = 50.0 + 124.03149777329222 * ((1.9694462586094064-({{{2}}}* pi / 180))
* sin(0.6010514667026994 * ({{{3}}} + 96) * pi / 180))
y = 50.0 + 1.6155950752393982 * 124.03149777329222 * 0.02613325650382181
- 1.6155950752393982 * 124.03149777329222 *
(1.3236744353715044 - (1.9694462586094064-({{{2}}}* pi / 180))
* cos(0.6010514667026994 * ({{{3}}} + 96) * pi / 180))
The flag of Navassa Island is simply the United States flag. It does not have a "local" flag or "unofficial" flag; it is an uninhabited island. The version with a profile view was based on Flags of the World and as a fictional design has no status warranting a place on any Wiki. It was made up by a random person with no connection to the island, it has never flown on the island, and it has never received any sort of recognition or validation by any authority. The person quoted on that page has no authority to bestow a flag, "unofficial" or otherwise, on the island.
Black up-pointing triangle ▲, U+25B2 from Unicode-Block Geometric Shapes (25A0–25FF)
Autor: Archer1742, Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Mount Rainier (a Stratovolcano), as viewed from the Sourdough Ridge trail.
Autor: Carport, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Physical location map of Washington, USA