Półkula mózgu
Półkula mózgu (łac. hemispherium cerebri) – parzysta część kresomózgowia. Półkule oddziela szczelina podłużna mózgu (fissura longitudinalis cerebri), zaś połączenie nerwowe zapewnia ciało modzelowate. Każda z półkul zawiera zewnętrzną warstwę istoty szarej, zwanej korą mózgu oraz wewnętrzną warstwę istoty białej.
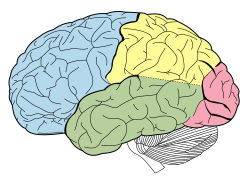
W strukturze makroskopowej półkul wyróżnia się powierzchnie: górno-boczną, przyśrodkową i dolną (podstawną) oraz brzegi: górny, dolno-przyśrodkowy i dolno-boczny. Powierzchnie półkul są pokryte bruzdami (sulci), które ograniczają zakręty (gyri). Bruzda środkowa i boczna występujące na powierzchni górno-bocznej półkul dzielą je na następujące parzyste płaty:
- płat czołowy – z ośrodkiem ruchowym i ruchowym mowy (ośrodek Broki)
- płat skroniowy – z ośrodkiem słuchu i czuciowym mowy (ośrodek Wernickego)
- płat ciemieniowy – z ośrodkiem czucia oraz korą integrującą, doznania czuciowe, wzrokowe i słuchowe
- płat potyliczny – z ośrodkiem wzroku
Na powierzchni przyśrodkowej półkul występuje także płat brzeżny (związany z uczeniem się i pamięcią). Dodatkowo jako szósty płat, wymienić należy znajdującą się w głębi bruzdy bocznej wyspę.
W płacie czołowym występują ośrodki kojarzące, które są miejscem powstawania myśli i pojęć.
W korze mózgowej znajdują się liczne skupiska neuronów – tzw. ośrodki korowe.
Bibliografia
- Adam Bochenek, Michał Reicher: Anatomia człowieka – Tom IV: Układ nerwowy ośrodkowy. Warszawa: PZWL, 2000. ISBN 83-200-2398-X.
![]() Przeczytaj ostrzeżenie dotyczące informacji medycznych i pokrewnych zamieszczonych w Wikipedii.
Przeczytaj ostrzeżenie dotyczące informacji medycznych i pokrewnych zamieszczonych w Wikipedii.
Media użyte na tej stronie
Star of life, blue version. Represents the Rod of Asclepius, with a snake around it, on a 6-branch star shaped as the cross of 3 thick 3:1 rectangles.
Design:
The logo is basically unicolor, most often a slate or medium blue, but this design uses a slightly lighter shade of blue for the outer outline of the cross, and the outlines of the rod and of the snake. The background is transparent (but the star includes a small inner plain white outline). This makes this image usable and visible on any background, including blue. The light shade of color for the outlines makes the form more visible at smaller resolutions, so that the image can easily be used as an icon.
This SVG file was manually created to specify alignments, to use only integers at the core 192x192 size, to get smooth curves on connection points (without any angle), to make a perfect logo centered in a exact square, to use a more precise geometry for the star and to use slate blue color with slightly lighter outlines on the cross, the rod and snake.
Finally, the SVG file is clean and contains no unnecessary XML elements or attributes, CSS styles or transforms that are usually added silently by common SVG editors (like Sodipodi or Inkscape) and that just pollute the final document, so it just needs the core SVG elements for the rendering. This is why its file size is so small.The Star of Life, medical symbol used on some ambulances.
Star of Life was designed/created by a National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (US Gov) employee and is thus in the public domain.Principal fissures and lobes of the cerebrum viewed laterally. Figure 728 from Gray's Anatomy with labels removed.