Port lotniczy Londyn-Gatwick
| |||||
(c) Pam Brophy, CC BY-SA 2.0 Terminal południowy | |||||
| Państwo | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kraj | |||||
| Miejscowość | Crawley | ||||
| Typ | cywilne | ||||
| Właściciel | Global Infrastructure Partners | ||||
| Kod IATA | LGW | ||||
| Kod ICAO | EGKK | ||||
| Strefa czasowa | UTC 0 | ||||
| Wysokość | 59 m n.p.m. | ||||
| Statystyki ruchu (2015[1]) | |||||
| Liczba pasażerów | 40 269 087 | ||||
| Liczba operacji | 267 760 | ||||
| Drogi startowe | |||||
| |||||
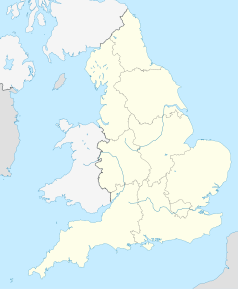
Położenie na mapie West Sussex Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crown copyright and database right, CC BY-SA 3.0 | |||||
Położenie na mapie Wielkiej Brytanii (c) Karte: NordNordWest, Lizenz: Creative Commons by-sa-3.0 de | |||||
| Strona internetowa | |||||
Port lotniczy Londyn-Gatwick (ang. London Gatwick Airport, kod IATA: LGW, kod ICAO: EGKK) – drugi najruchliwszy międzynarodowy port lotniczy Londynu (po Heathrow). Położony jest 40 km na południe od centrum stolicy Wielkiej Brytanii i 40 km na północ od miasta Brighton znajdującego się nad kanałem La Manche, między miejscowościami Horley a Crawley.
W 2005 obsłużył około 32,6 mln pasażerów[2], którzy podróżowali do i z około 200 miast. Linie czarterowe nie mogą w zasadzie korzystać z Heathrow, dlatego wiele z nich korzysta z Gatwick jako swojej bazy. Port Lotniczy Londyn-Gatwick obsługuje również wiele lotów do i z USA – ze względu na ograniczenia lotów transatlantyckich na Heathrow. Lotnisko jest drugim węzłem British Airways i Virgin Atlantic.
Terminale
Lotnisko posiada dwa terminale: Północny i Południowy.
Terminal Północny
Budowa rozpoczęła się w 1983 roku. Terminal został otwarty przez królową Elżbietę II w 1988 roku. W 1991 roku został rozbudowany.
Terminal Południowy
Początki terminalu datuje się na lata 1956-1958. Następne rozbudowy to lata 1962, 1983 i 1985. Obecnie realizowany jest program odnowy południowego terminalu.
Kierunki lotów i linie lotnicze
Gatwick Airport Transit
Gatwick Airport Transit to zautomatyzowany wagonowy system transportowy typu people mover, dostarczający darmowe połączenie pomiędzy południowym i północnym terminalem. System składa się z dwóch 3-wagonowych pojazdów, przemieszczających się po specjalnie przygotowanej, długiej na 1,2 km trasie-estakadzie. Pojazdy są w pełni automatyczne, bez kierowców. Pociągi odjeżdżają co kilka minut, sama podróż trwa około 3-4 minut. W jej czasie możemy posłuchać automatycznie generowanych informacji o nowych połączeniach lotniczych z poszczególnych terminali.
Przypisy
- ↑ http://www.caa.co.uk/Data-and-analysis/UK-aviation-market/Airports/Datasets/
- ↑ Statystyki przewozów w brytyjskich portach lotniczych według CAA za 2005 (ang.)
- ↑ Rossiya/Aeroflot adds St. Petersburg – London service in S18 :: Routesonline, www.routesonline.com [dostęp 2018-03-17] (ang.).
- ↑ Air Italy - Timetable, www.airitaly.com [dostęp 2018-03-17].
- ↑ Qatar Airways to return to London Gatwick on May 22 - Business Traveller – The leading magazine for frequent flyers, www.businesstraveller.com [dostęp 2018-04-13] (ang.).
- ↑ WestJet heads to Paris and London from Halifax - Jan 29, 2018, westjet2.mediaroom.com [dostęp 2018-03-17].
Linki zewnętrzne
Media użyte na tej stronie
(c) Karte: NordNordWest, Lizenz: Creative Commons by-sa-3.0 de
Location map of the United Kingdom
Redirect arrow, to be used in redirected articles in Wikipedias written from left to right. Without text.
Flag of England. Saint George's cross (a red cross on a white background), used as the Flag of England, the Italian city of Genoa and various other places.
Icon representing an increase, consisting of a green-colored, up-pointing triangle.
Symbol lotniska do legendy mapy
Autor: Pedro A. Gracia Fajardo, escudo de Manual de Imagen Institucional de la Administración General del Estado, Licencja: CC0
Flaga Hiszpanii
Łatwo można dodać ramkę naokoło tej grafiki
Flag of Portugal, created by Columbano Bordalo Pinheiro (1857-1929), officially adopted by Portuguese government in June 30th 1911 (in use since about November 1910). Color shades matching the RGB values officially reccomended here. (PMS values should be used for direct ink or textile; CMYK for 4-color offset printing on paper; this is an image for screen display, RGB should be used.)
The flag of Navassa Island is simply the United States flag. It does not have a "local" flag or "unofficial" flag; it is an uninhabited island. The version with a profile view was based on Flags of the World and as a fictional design has no status warranting a place on any Wiki. It was made up by a random person with no connection to the island, it has never flown on the island, and it has never received any sort of recognition or validation by any authority. The person quoted on that page has no authority to bestow a flag, "unofficial" or otherwise, on the island.
Flag of Jamaica. “The sunshine, the land is green, and the people are strong and bold” is the symbolism of the colours of the flag. GOLD represents the natural wealth and beauty of sunlight; GREEN represents hope and agricultural resources; BLACK represents the strength and creativity of the people. The original symbolism, however, was "Hardships there are, but the land is green, and the sun shineth", where BLACK represented the hardships being faced.
The flag of the Dominican Republic has a centered white cross that extends to the edges. This emblem is similar to the flag design and shows a bible, a cross of gold and 6 Dominican flags. There are branches of olive and palm around the shield and above on the ribbon is the motto "Dios,Patria!, Libertad" ("God, Country, Freedom") and to amiable freedom. The blue is said to stand for liberty, red for the fire and blood of the independence struggle and the white cross symbolized that God has not forgotten his people. "Republica Dominicana". The Dominican flag was designed by Juan Pablo Duarte, father of the national Independence of Dominican Republic. The first dominican flag was sewn by a young lady named Concepción Bona, who lived across the street of El Baluarte, monument where the patriots gathered to fight for the independence, the night of February 27th, 1844. Concepción Bona was helped by her first cousin María de Jesús Pina.
Flag of Albania
Flag of Gibraltar
Flag of Maldives. The colours used are Pantone 186 C for red and Pantone 348 C for green.
Flag of Israel. Shows a Magen David (“Shield of David”) between two stripes. The Shield of David is a traditional Jewish symbol. The stripes symbolize a Jewish prayer shawl (tallit).
Flaga Finlandii
Flag of the Turks and Caicos Islands
Autor: Felicity and Phillip z Wellington, New Zealand, Licencja: CC BY 2.0
Arriving from Sevilla
Gatwick, 5 October 2005
(c) Pam Brophy, CC BY-SA 2.0
South Terminal, London Gatwick Airport. Taken from Norfolk House in the South Terminal building, overlooking the loading bays.
Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crown copyright and database right, CC BY-SA 3.0
Map of West Sussex, UK with the following information shown:
- Administrative borders
- Coastline, lakes and rivers
- Roads and railways
- Urban areas
Equirectangular map projection on WGS 84 datum, with N/S stretched 155%
Geographic limits:
- West: 1.01W
- East: 0.10E
- North: 51.20N
- South: 50.70N
Flag of Rwanda. The flag ratio is 2:3 with the stripes being 2:1:1. Colors are the following officially: Pantone 299 C 2X (blue), RAL 6029 (green), RAL 1023 (yellow) and RAL 1003 (golden yellow). (As of 03/08/2010, the only color used is the Pantone 299 C, which is from here. The rest of the colors are RAL shades from here.)