Pratt & Whitney JT9D
| ||
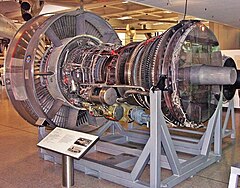 JT9D | ||
| Dane podstawowe | ||
| Typ | turbowentylatorowy | |
|---|---|---|
| Kraj pochodzenia | ||
| Producent | Pratt & Whitney | |
| Pierwsze testy | grudzień 1966 | |
| Zastosowanie | Boeing 747 Boeing 767 Airbus A310 McDonnell Douglas DC-10 | |
| Rozwinięto w model | Pratt & Whitney PW4000 | |
| Dane techniczne | ||
| Średnica | 2,37 m | |
| Długość | 3,37 m | |
| Masa | 3905 kg | |
| Osiągi | ||
| Ciąg | 213,5,5 kN – 250 kN | |

JT9D – turbowentylatorowy silnik lotniczy produkowany przez amerykańską firmę Pratt & Whitney do zastosowania na samolotach szerokokadłubowych[1]. Pierwsze testy silników rozpoczęto w grudniu 1966, które później zostały zamontowane po raz pierwszy na Boeingu 747-100.
Projekt
Silnik JT9D został opracowany w ramach projektowania samolotu Lockheed C-5 Galaxy. Lockheed zwrócił się do Pratt & Whitney aby zaprojektować nowy duży silnik lotniczy do C-5 Galaxy, jednak ostatecznie Lockheed wybrał silniki General Electric TF39. Jednak silnik JT9D został wybrany przez Boeinga do napędzania nowych Boeingów 747[1], którego pierwszy lot odbył się 9 lutego 1969, zaś pierwsze próby w powietrzu rozpoczęły się w czerwcu 1968 przy pomocy samolotu B-52.
Silnik JT9D-3 wszedł do służby w 1970. Został Zbudowany z wykorzystaniem tytanu i stopów niklu. Zastosowano jeden wentylator, trzystopniową sprężarkę niskiego ciśnienia oraz jedenastostopniową sprężarkę wysokiego ciśnienia połączoną z dwustopniową turbiną wysokiego ciśnienia i czterostopniową turbiną niskiego ciśnienia. Ta wersja JT9D ważyła 3905 kg i wytwarzała maksymalny ciąg 193 kN. Produkcję JT9D-3 zakończono w 1990.
Następcą udanych silników JT9D jest silnik Pratt & Whitney PW4000, który składa się z mniejszej ilości elementów, jest bardziej niezawodny oraz jego cena zakupu jest niższa od poprzednika.
Warianty
- JT9D-3
- JT9D-3A
- JT9D-7A/F/J
- JT9D-7Q
- JT9D-7R4
- JT9D-7AH
Zastosowane w samolotach
Przypisy
Media użyte na tej stronie
The flag of Navassa Island is simply the United States flag. It does not have a "local" flag or "unofficial" flag; it is an uninhabited island. The version with a profile view was based on Flags of the World and as a fictional design has no status warranting a place on any Wiki. It was made up by a random person with no connection to the island, it has never flown on the island, and it has never received any sort of recognition or validation by any authority. The person quoted on that page has no authority to bestow a flag, "unofficial" or otherwise, on the island.
Autor: Cliff from I now live in Arlington, VA (Outside Washington DC), USA, Licencja: CC BY 2.0
The Pratt & Whitney JT9D turbofan was developed to power the current generation of wide-body commercial jets. It first ran in 1966, was flight tested in 1968, and received FAA certification in 1969.
JT9D engines powered the Boeing 747 on its first flight on February 9, 1969, and entered airline service in 1970. The JT9D also powered some versions of the McDonnell Douglas DC-10, and Airbus Industrie A300 and A310.
An advanced design, the JT9D was the first of the very large, high bypass ratio turbofans in commercial service. The JT9D displayed here is a pre-production engine built for ground testing rather than for flight, although it is outwardly identical to production examples.
collections.nasm.si.edu/code/emuseum.asp?profile=objects&...Autor: user:Jaypee, Licencja: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Pratt & Whitney JT9D im Deutsches Museum München


