Rezystancja dynamiczna
Rezystancja dynamiczna (oporność przyrostowa) – oporność dla składowej zmiennej prądu w warunkach pracy małosygnałowej. W elemencie nieliniowym opisuje zmiany zachodzące w otoczeniu obranego punktu pracy.
Rezystancję dynamiczną opisuje wzór:
gdzie:
- – przyrosty napięć i natężeń w otoczeniu obranego punktu pracy,
- – kąt nachylenia stycznej do wykresu przechodzącej przez obrany punkt pracy do osi poziomej,
- – współczynnik proporcjonalności zależny od obranego układu jednostek.
- – kąt nachylenia stycznej do wykresu przechodzącej przez obrany punkt pracy do osi poziomej,
Rezystancja dynamiczna informuje o wartości przyrostu prądu w elemencie przy określonej zmianie napięcia. Dla elementów liniowych takich jak rezystor jest ona zawsze taka sama i równa rezystancji statycznej, dla elementów nieliniowych (np. dioda półprzewodnikowa, warystor) jest ona zmienna, zależy od wartości prądu i napięcia stałego określającego punkt pracy elementu.
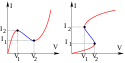
Ujemna rezystancja dynamiczna
Niektóre elementy nieliniowe (np. dioda tunelowa, bareter, lampa neonowa) mogą wykazywać lokalną ujemną rezystancję dynamiczną (niemniej jednak w każdym punkcie charakterystyki rezystancja statyczna jest dodatnia).
Zobacz też
Bibliografia
- Andrzej Syrzycki: Laboratorium elektrotechniki. Warszawa: Oficyna Wydawnicza Politechniki Warszawskiej, 1999, s. 48. ISBN 83-7207-126-8.
Media użyte na tej stronie
Autor: Д.Ильин: vectorization, Licencja: CC0
Current-voltage characteristics or IV curves showing two types of negative differential resistance.
The left graph shows voltage controlled negative resistance (VCNR) also called N type. In this type the voltage is a multivalued function of current, but the current is a single-valued function of voltage. The graph is shaped vaguely like the letter N, with a voltage region with negative resistance between two positive resistance regions. Electronic devices with this type of negative resistance include the tunnel diode, Gunn diode, and vacuum tubes operating in the "dynatron" mode.
The right graph shows current controlled negative resistance (CCNR) also called S type. In this type the voltage is a multivalued function, while the current is a single-valued function. The graph is shaped vaguely like the letter S, with a region of current with negative resistance between to regions with positive resistance. Devices with this type of negative resistance include the IMPATT diode, unijunction transistor, SCR, and gas-discharge tubes like neon lamps and fluorescent tubes.