Wielkie Księstwo Oldenburga
| 1815–1918 | |||||
| |||||
| Język urzędowy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stolica | |||||
| Ustrój polityczny | |||||
| Typ państwa | |||||
| Głowa państwa | |||||
| Powierzchnia • całkowita |
| ||||
| Liczba ludności (1925) • całkowita • gęstość zaludnienia |
| ||||
| Proklamacja republiki | 1918 | ||||
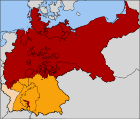
 Mapa Oldenburga wraz z dwoma eksklawami: Birkenfeld i Eutin w ramach Cesarstwa Niemieckiego (1871-1918). | |||||
Księstwo Oldenburga, formalnie od 1815, a faktycznie od 1829 Wielkie Księstwo Oldenburga (niem. Großherzogtum Oldenburg)[1] – historyczne państwo niemieckie powstałe w 1815 roku z ziem dawnego Księstwa Oldenburga (państwo Świętego Cesarstwa Rzymskiego) włączonego w 1810 roku do Cesarstwa Francuskiego. Księstwo składało się z trzech oddzielnych terytoriów – Oldenburga i dwóch eksklaw: Birkenfeld (wcielonej w 1937 do Prus w zamian za Wilhelmshaven) i Eutin.
Historia
W 1815 państwo na kongresie wiedeńskim uzyskało status wielkiego księstwa i ziemie Birkenfeld oraz Eutin. Tytuł wielkiego księcia nie był używany przez władców aż do 1829 roku i państwo do tego czasu nazywane było księstwem. W 1815 roku Oldenburg wszedł w skład Związku Niemieckiego. W 1866 roku wszedł w skład Związku Północnoniemieckiego, a po zjednoczeniu Niemiec w 1871 roku stał się jednym z krajów Cesarstwa Niemieckiego.
W wyniku rewolucji listopadowej w 1918 i obaleniu monarchii państwo przekształcono w republikę, 11 listopada 1918 roku wielki książę Fryderyk August II abdykował i wyjechał do zamku w Rastede.
Po 1945 kraj włączono do Dolnej Saksonii. W styczniu 1975 mieszkańcy Oldenburga (873 tys. osób) wraz z mieszkańcami Schaumburg-Lippe opowiedzieli się za przekształceniem ich okręgów w landy RFN, czego jednak Bundestag nie zaakceptował, skłaniając się raczej ku redukcji liczby krajów z 10 do 5-6[2].
Wielcy książęta Oldenburga
Zobacz też
Przypisy
Bibliografia
- Karl Georg Böse, Das Großherzogtum Oldenburg. Topographisch-statistische Beschreibung desselben, 1863 (wznowienie: Wenner, Osnabrück 1979)
- Paluszyński Tomasz, Historia Niemiec i państw niemieckich. Zarys dziejów politycznych, Oficyna Wydawnicza Wyższej Szkoły Języków Obcych w Poznaniu, Poznań 2006
Media użyte na tej stronie
Flaga Niemiec o proporcjach 3:2
Flag of the duchy of Saxe-Coburg & Gotha 1911-1920; Ratio (2:3)
Flag of the Kingdom of Württemberg; Ratio (3:5)
Flag of the Grand Duchy of Baden 1855-1891; Ratio (3:5)
Flag of the duchy of Saxe-Coburg & Gotha 1826-1911; Ratio (2:3)
Flag of Alsace-Lorraine, adopted on the 25th of June 1912 and flag of the Republic of Alsace-Lorraine (Nov 11 1918 - Nov 21 1918)
Flag of the Duchy of Anhalt and also flag of Augsburg
Flag of the principality of Reuß Younger Line; Ratio (4:5) may also be (5:6)
Flag of the principality of Lippe; Ratio (2:3)
Flag of the Grand Duchies of Mecklenburg-Strelitz and Mecklenburg-Schwerin; Ratio (2:3)
Autor: User:52 Pickup, Licencja: CC BY-SA 2.5
The North German Confederation / Norddeutscher Bund (1867–1871) in red. The states that would join the confederation and form the German Empire are in orange. Alsace-Lorraine, the territory annexed from France following the Franco-Prussian War of 1871, is in a paler orange.
Autor: Milenioscuro, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Locator map of Oldenburg in the German Empire
Autor: Jacques63, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Coats of arms Grand Duché d Oldenbourg
Flag of the Grand Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach 1813-1897; Ratio (2:3)
Flag of the principalities of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen and Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt; Ratio (2:3)
Flag of the Kingdom of Saxony; Ratio (2:3)
Flag of the Grand Duchy of Hesse without arms; Ratio (4:5)
Civil flag of Oldenburg, before 1871 and beween 1921 and 1935
Flag of the principality of Schaumburg-Lippe; Ratio (2:3), c. 1880–1935
Flag of the duchy of Brunswick; Ratio (2:3)
Imperial Eagle of the German Empire from 1889 to 1918.
Flag of the principality of Reuss Elder Line; Ratio (27:34)