Wyżyny Appalaskie
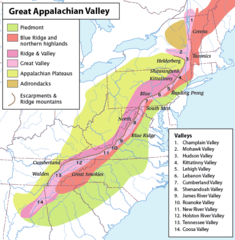 Regionalizacja fizycznogeograficzna Appalachów; Wyżyny Appalaskie zaznaczone jaśniejszym odcieniem koloru zielonego | |
| Państwo | |
|---|---|
| Rodzaj obiektu | |
Wyżyny Appalaskie[1] (ang. Appalachian Plateau lub Appalachian Plateaus) – pas wyżyn we wschodniej części Stanów Zjednoczonych, biegnący wzdłuż łańcucha górskiego Appalachów, po jego zachodniej stronie. Rozciąga się od terytorium stanu Nowy Jork na północnym wschodzie, przez Pensylwanię, Wirginię Zachodnią, Ohio, Kentucky i Tennessee, po Alabamę na południowym zachodzie[2][3]. Niewielkie fragmenty znajdują się także w granicach stanów Maryland[4], Wirginia[2] i Georgia[5].
W obrębie Wyżyn Appalaskich wyszczególnia się wyżyny Allegheny i Cumberland[6] oraz pasma górskie Catskill, Pocono, Allegheny i Cumberland. Obszar wyżyn zbudowany jest ze skał osadowych, w tym piaskowców, zlepieńców i łupków, nagromadzonych w erze paleozoicznej[3]. Urozmaicona rzeźba terenu jest wynikiem procesów fluwialnych[6].
Znajdują się tu największe na terenie Stanów Zjednoczonych złoża węgla, a także znaczne złoża wapienia, rud żelaza (w dużym stopniu wyeksploatowane[5]), ropy naftowej i gazu ziemnego[3].
Przypisy
- ↑ Urzędowy wykaz polskich nazw geograficznych świata. Główny Urząd Geodezji i Kartografii, 2019. s. 598. [dostęp 2022-10-09].
- ↑ a b Appalachian Plateau, [w:] Encyclopædia Britannica [online] [dostęp 2022-10-09] (ang.).
- ↑ a b c Appalachian Plateaus Province. National Park Service. [dostęp 2022-10-09]. (ang.).
- ↑ Maryland at a Glance – Geology. Maryland.gov. [dostęp 2022-10-09]. (ang.).
- ↑ a b Appalachian Plateau Geologic Province. New Georgia Encyclopedia. [dostęp 2022-10-09]. (ang.).
- ↑ a b Brooks Mitchell: Appalachian Plateau Geology and Landmarks. ThoughtCo.. [dostęp 2022-10-09]. (ang.).
Media użyte na tej stronie
Autor: Uwe Dedering, Licencja: CC BY-SA 3.0
Relief location map of the USA (without Hawaii and Alaska).
EquiDistantConicProjection : Central parallel :
* N: 37.0° N
Central meridian :
* E: 96.0° W
Standard parallels:
* 1: 32.0° N * 2: 42.0° N
Made with Natural Earth. Free vector and raster map data @ naturalearthdata.com.
Formulas for x and y:
x = 50.0 + 124.03149777329222 * ((1.9694462586094064-({{{2}}}* pi / 180))
* sin(0.6010514667026994 * ({{{3}}} + 96) * pi / 180))
y = 50.0 + 1.6155950752393982 * 124.03149777329222 * 0.02613325650382181
- 1.6155950752393982 * 124.03149777329222 *
(1.3236744353715044 - (1.9694462586094064-({{{2}}}* pi / 180))
* cos(0.6010514667026994 * ({{{3}}} + 96) * pi / 180))
The flag of Navassa Island is simply the United States flag. It does not have a "local" flag or "unofficial" flag; it is an uninhabited island. The version with a profile view was based on Flags of the World and as a fictional design has no status warranting a place on any Wiki. It was made up by a random person with no connection to the island, it has never flown on the island, and it has never received any sort of recognition or validation by any authority. The person quoted on that page has no authority to bestow a flag, "unofficial" or otherwise, on the island.
Autor:
- Greatvalley-map.jpg: Pfly
- derivative work: Perhelion (talk)
Map of the Appalachian Mountain physiographic regions, highlighting the Great Appalachian Valley, naming the main valleys making it up and the main mountains on either side.
Legend:
- Piedmont
- Blue Ridge Mountains and Northern Highlands
- Ridge and Valley
- Great Valley
- Appalachian Plateaus
- Adirondacks
- Escarpments and Ridge Mountains